Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Salidroside is a bioactive phenolic glycoside compound isolated from Rhodiola rosea and is a prolyl endopeptidase inhibitor. Salidroside can alleviate cachexia symptoms in a tumor cachexia mouse model by activating mTOR signaling and protect dopaminergic neurons by enhancing PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitochondrial autophagy. Salidroside can also inhibit the growth of cancer cells by regulating the CDK4-cyclin D1 pathway to block the G1 phase and/or regulating the Cdc2-cyclin B1 pathway to block the G2 phase.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $78 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $139 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $198 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $297 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $453 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $53 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Salidroside is a bioactive phenolic glycoside compound isolated from Rhodiola rosea and is a prolyl endopeptidase inhibitor. Salidroside can alleviate cachexia symptoms in a tumor cachexia mouse model by activating mTOR signaling and protect dopaminergic neurons by enhancing PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitochondrial autophagy. Salidroside can also inhibit the growth of cancer cells by regulating the CDK4-cyclin D1 pathway to block the G1 phase and/or regulating the Cdc2-cyclin B1 pathway to block the G2 phase. |
| In vitro | METHODS: Min6 cells were co-treated with salidroside (Rhodioloside) (50 μM, 3 days), glucose or H2O2, and the changes in protein levels in β cells were detected by western blot. RESULTS Salidroside downregulated the expression of NOX2 and inhibited the subsequent activation of JNK and caspase 3, thereby preventing β cell death. [4] METHODS: SH-SY5Y cells were treated with Salidroside (Rhodioloside) (25-100 μM, 24 hours) and then exposed to MPP+ (500 μM, 24 hours). Cell viability was determined by MTT assay, cell apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry, and cell morphology was evaluated by Hoechst staining. RESULTS Salidroside concentration-dependently prevented the decrease in cell viability induced by MPP+; Salidroside concentration-dependently significantly reduced the number of MPP+-treated annexin V/PI-stained cells; in Hoechst staining, Salidroside significantly inhibited the MPP+-induced increase in chromatin condensation, hyperfluorescence, and nuclear fragmentation in SH-SY5Y cells. [5] METHODS: siDJ-1 transfected H-SY5Y cells were treated with Salidroside (25-100 μM, 24 hours), and then treated with MPP+ (500 μM, 24 hours). , the mRNA expression of DJ-1, Nrf2, GCLc, SOD1 and SOD2 was determined and statistically analyzed. RESULTS Silencing of DJ-1 significantly inhibited the Salidroside-induced increase in mRNA and protein levels (DJ-1, Nrf2, GCLc, SOD1 and SOD2) in MPP+-treated SH-SY5Y cells; silencing DJ-1 also significantly Significantly inhibited the Salidroside-induced decrease in ROS levels and increase in GSH levels in MPP+-treated cells. [5] |
| In vivo | METHODS: Salidroside (Rhodioloside) (100 mg, oral, once a day. 5 weeks) was used to treat db/db mice after 10 weeks of HFD, and its effect on db/db mice with prediabetes at 4 weeks was observed; after 5 weeks of treatment , conduct OGTT experiment RESULTS Salidroside could not significantly alleviate the elevated blood glucose in db/db mice within the first 15 days; Salidroside protected db/db mice from severe hyperglycemia after 21 days of treatment; Salidroside-treated db/db mice were less Rats' tolerance to glucose was significantly improved. [4] |
| Synonyms | Rhodioloside |
| Molecular Weight | 300.30 |
| Formula | C14H20O7 |
| Cas No. | 10338-51-9 |
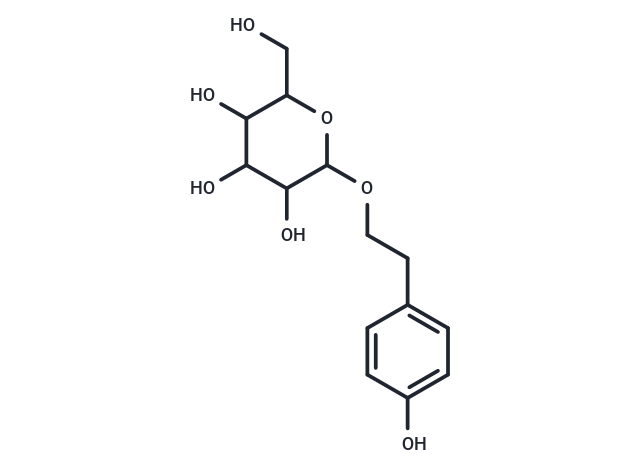
| Smiles | OCC1OC(OCCc2ccc(O)cc2)C(O)C(O)C1O |
| Relative Density. | 1.46 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 55.00 mg/mL (183.15 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 4.00 mg/mL (13.32 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 55.00 mg/mL (183.15 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: 5 mg/mL (16.65 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO/H2O
DMSO/H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.