Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Oxibendazole is a benzimidazole drug that interferes with metabolic pathways, used to protect against roundworms, strongyles, threadworms, pinworms and lungworm infestations in horses and some domestic pets.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 33.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 50.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 75.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 129.00 | |
| 200 mg | In stock | $ 197.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 35.00 |

| Description | Oxibendazole is a benzimidazole drug that interferes with metabolic pathways, used to protect against roundworms, strongyles, threadworms, pinworms and lungworm infestations in horses and some domestic pets. |
| In vitro | BRL-15572 displays high affinity and selectivity for h5-HT1D receptors. BRL-15572 has 60-fold higher affinity for h5-HT1D than 5-HT1B receptors. BRL-15572 binds to h5-HT1B and h5-HT1D receptors with pKB of less than 6 and 7.1, respectively. BRL-15572 stimulates [35S]GTP γ S binding in both cell lines, with potencies that correlated with their receptor binding affinities in both h5-HT1B and h5-HT1D receptor expressing cell lines. BRL-15572 reveals receptor binding affinities for 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1E, 5-HT1F, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C, 5-HT6 and 5-HT7 with pKi of 7.7, 6.1, 5.2, 6.0, 6.6, 7.4, 6.2, 5.9 and 6.3, respectively. In the h5-HT1D cell line, both BRL-15572 (1 μM) shifts the 5-HT concentration response curve with pKB of 7.1, respectively. BRL-15572 does have moderately high affinity at human 5-HT1A and 5-HT2B receptors. [1] In human atrial appendages, the electrically evoked tritium overflow is inhibited by 5-HT in a manner susceptible to antagonism by BRL-15572 (300 nM; 23 times Ki at h5-HT1D receptors). [2] The inhibitory effect of 5-HT on the K+-evoked overflow of glutamate is antagonized by the h5-HT1D receptor ligand BRL-15572. BRL-15572 (1 μM) is unable to modify the effect of 5-HT at the autoreceptor regulating [3H]5-HT release. [3] The selective 5-HT1D/1B receptor antagonist BRL 15572 inhibits the effect of the agonist L-694 247. [4] |
| In vivo | Oxibendazole shows a significant reduction of the proportion of positive foals after treatment. Oxibendazole significantly reduces the proportion of positive horse foals on six of the seven farms (86%). [1] Oxibendazole reduces in the number of strongyle eggs/g (epg) in horse, but the reduction is only by 82% with an upper confidence limit of 89%. [2] Oxibendazole results in collapse of the lip papillae, rupture of buccal cavity cuticle, prolapse of the pharynx, degeneration of epithelial cells and erosion of microvilli in adult Ascaris suum, theses changes may lead to impaired digestion and absorption of nutrients and cause cellular autolysis, resulting in the death of the worm. [3] Oxibendazole reduces faecal worm egg counts (EPG) by 97.6% for Toxocara canis, 95.7% for Trichuris vulpis, 94.6% for Ancylostoma caninum, and 100% for Toxascaris leonine in dogs and cats. [4] Oxibendazole could only be detected in plasma at the 0.5 hours and 1.0 hours post administration sampling times and the mean maximum plasma concentration is 0.008 mg/mL in horse. Oxibendazole is detected in faeces between 12 and 72 hours after administration and the highest dry faecal concentration was detected at 24 hours. [5] |
| Molecular Weight | 249.27 |
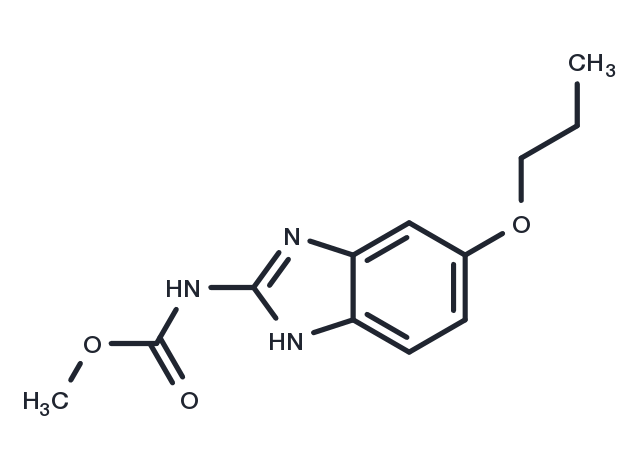
| Formula | C12H15N3O3 |
| CAS No. | 20559-55-1 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 30 mg/ml (120.35 mM)
H2O: Insoluble
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Oxibendazole 20559-55-1 Apoptosis Microbiology/Virology Parasite Inhibitor inhibit inhibitor
