Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid (AC-ASP-OH) is a derivative of aspartic acid. It is the second most concentrated molecule in the brain after the amino acid glutamate. It is synthesized in neurons from the amino acid aspartate and acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA). The various functions served by N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid (AC-ASP-OH) are still under investigation, but the primary proposed functions include (1) acting as a neuronal osmolyte that is involved in fluid balance in the brain, (2) serving as a source of acetate for lipid and myelin synthesis in oligodendrocytes (the glial cells that myelinate neuronal axons), (3) serving as a precursor for the synthesis of the important dipeptide neurotransmitter N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG), and (4) playing a potential role in energy production from the amino acid glutamate in neuronal mitochondria.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 41.00 | |
| 200 mg | In stock | $ 59.00 |


| Description | N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid (AC-ASP-OH) is a derivative of aspartic acid. It is the second most concentrated molecule in the brain after the amino acid glutamate. It is synthesized in neurons from the amino acid aspartate and acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA). The various functions served by N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid (AC-ASP-OH) are still under investigation, but the primary proposed functions include (1) acting as a neuronal osmolyte that is involved in fluid balance in the brain, (2) serving as a source of acetate for lipid and myelin synthesis in oligodendrocytes (the glial cells that myelinate neuronal axons), (3) serving as a precursor for the synthesis of the important dipeptide neurotransmitter N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG), and (4) playing a potential role in energy production from the amino acid glutamate in neuronal mitochondria. |
| Synonyms | AC-ASP-OH, N-Acetylaspartic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 175.14 |
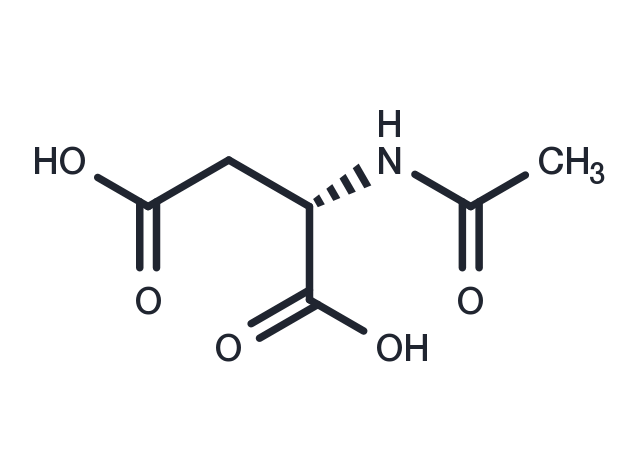
| Formula | C6H9NO5 |
| CAS No. | 997-55-7 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 3.33 mg/mL (19.03 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid 997-55-7 Metabolism Others Endogenous Metabolite N Acetyl L aspartic acid NAcetylLaspartic acid AC-ASP-OH Inhibitor N-Acetylaspartic acid inhibit inhibitor
