Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Enalaprilat Dihydrate (MK-422 Dihydrate) (IC50=1.94 nM) is a potent angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $33 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $47 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $84 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $142 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $105 | In Stock |
| Description | Enalaprilat Dihydrate (MK-422 Dihydrate) (IC50=1.94 nM) is a potent angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. |
| Targets&IC50 | ACE:1.94 nM |
| In vitro | Enalaprilat has high affinity for human endothelial ACE with IC50 of 1.94 nM in vitro binding assay by displacing a saturating concentration of [125I]351A, a radiolabeled lisinopril analogue from ACE binding sites, and shows bradykinin/angiotensin I selectivity ratio of 1.00 calculated from double displacement experiments. [1] Enalaprilat has the strong inhibitory effect on Aβ42-to-Aβ40-converting activity found in the N-domain of ACE, exhibiting a 10-fold lower IC50 (0.003~0.01 μM) than captopril (0.03~0.1 μM). [2] Enalaprilat (100 nM) blocks protein kinase C epsilon by directly activating bradykinin B1 receptor at the canonical Zn2+ binding site, leading to prolonged nitric oxide (NO) production in cytokine-treated human lung microvascular endothelial cells. [3] Enalaprilat attenuates the IGF-I induced neonatal rat cardiac fibroblast growth (30% reduction) in a concentration-dependent fashion, with IC50 of 90 mM. [4] |
| In vivo | Enalaprilat has unfavourable ionisation characteristics to allow sufficient potency for oral administration, thus Enalaprilat is only suitable for intravenous administration, which is overcome by the esterification with ethanol to produce Enalapril. Administration of Enalaprilat induces a significant reduction of MAP at 70 minutes compared with the placebo group during haemorrhagic shock in rats, and results in a 50% reduction of CO, a general tendency of EB extravasation which is significant in the kidney and lungs, and a significant increase in ileal EB extravasation (53%). [5] Enalaprilat has no effect in nonhypertrophied hearts, but significantly attenuates the greater increase in left ventricular end-diastolic pressure in hypertrophied hearts compared with no drug. [6] |
| Kinase Assay | Single displacement binding assay: The binding assay is based on the competitive displacement of [125I]351A by Enalaprilat performed on whole endothelial cells. Subconfluent HUVECs in 6-well plates are rinsed with 2 mL binding buffer (140 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 1.8 mM CaCl2, 1.03 mM MgCl2, 0.42 mM NaH2PO4, 10 mM HEPES, 2 mM sodium pyruvate and 5 mM glucose, pH 7.4), and the culture medium is replaced with 2.5 mL fresh binding buffer containing 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS). The Enalaprilat (2.5-12.5 μL, 0.1-50 nM) or equivalent volumes of diluent are added to the binding buffer. A saturating amount of [125I]351A (10 μL, typically 106 cpm) is then added to each sample and the plates are incubated at 37 °C for 2 hours in a thermostatic bath. The cells are then rinsed twice with 1.5 mL binding buffer. Finally, the cells are extracted with 0.5 mL NaOH 1 N, incubated for 5 minutes, and the radioactivity is counted with a gamma counter. The ratio of specific [125I]351A bound to total bound activity (B/B0) is calculated, and the inhibitory potency of Enalaprilat expressed as the concentration of ACE inhibitors able to displace 50% of the bound radioligand, i.e. the IC50. |
| Cell Research | After 24 hours incubation in serum-free medium (DMEM), cells are stimulated with IGF-I (1-100 nM) and coincubated with Enalaprilat (1 nM-10 μM) for 24 hours. Cellular proliferation is assessed by 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation during the last 4 hours of the 24 hours incubation period using a colorimetric immunoassay. The extinctions are measured at 450 nm in an ELISA plate reader. All values consist of an n=9.(Only for Reference) |
| Alias | MK-422 Dihydrate |
| Molecular Weight | 348.4 |
| Formula | C18H24N2O5·2H2O |
| Cas No. | 84680-54-6 |
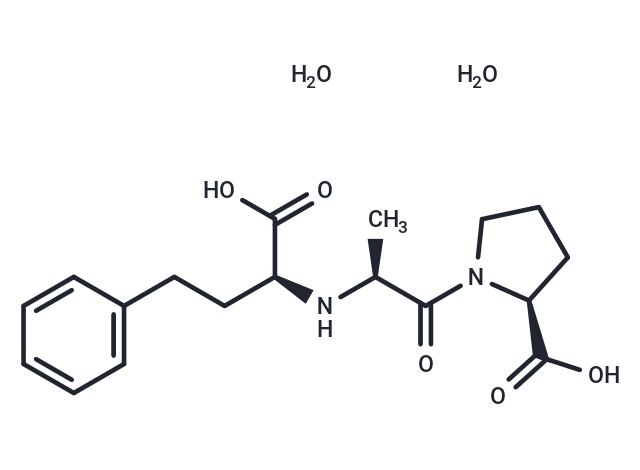
| Smiles | O.O.C[C@H](N[C@@H](CCc1ccccc1)C(O)=O)C(=O)N1CCC[C@H]1C(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | store at low temperature,keep away from moisture | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 70 mg/mL (200.92 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.