Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
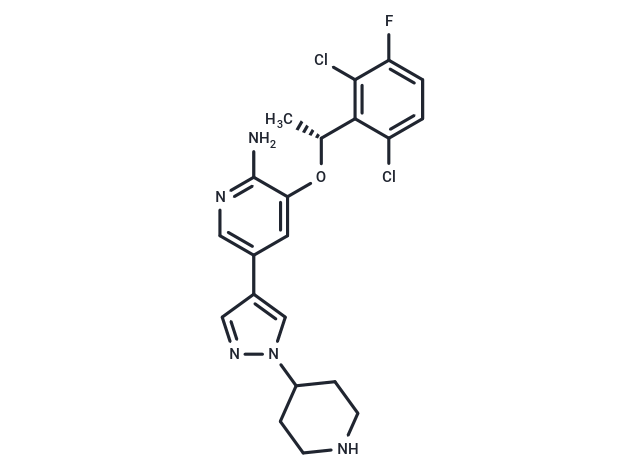
Crizotinib (PF-02341066) is an ATP-competitive small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor of c-MET (IC50: 8 nM) and ALK (IC50: 20 nM) receptors.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | Inquiry | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $29 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $44 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $53 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $62 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $85 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $158 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $48 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Crizotinib (PF-02341066) is an ATP-competitive small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor of c-MET (IC50: 8 nM) and ALK (IC50: 20 nM) receptors. |
| Targets&IC50 | c-Met:11 nM (A498 cells), c-Met (NCI-H69 cells):13 nM, EBC-1 cells:≤ 10 nM, V1092I cells:19 nM, ALK:24 nM (cell free), ALK receptors:20 nM, H1094R cells:2 nM, H1993 cells:≤ 10 nM, Y1230C cells:127 nM, M1250T cells:15 nM, Y1235D cells:92 nM, c-Met (HOP-92 cells):16 nM, ALK (ALCL cells):30 nM, NIH3T3 cells (expressing wild-type receptor):13 nM, mIMCD3 mouse or MDCK cells canine epithelial cell:5 nM and 20 nM |
| In vitro | Crizotinib (PF-2341066) potently inhibited c-Met phosphorylation and c-Met-dependent proliferation, migration, or invasion of human tumor cells in vitro (IC50: 5-20 nmol/L). In addition, PF-2341066 potently inhibited HGF-stimulated endothelial cell survival or invasion and serum-stimulated tubulogenesis in vitro [1]. Both of two cell lines with MET amplification, EBC-1, and H1993, were sensitive to crizotinib (IC50: 10 nM). In contrast, crizotinib did not substantially inhibit the proliferation of lung cancer cells with a MET mutation (H2122, H1437, and H596) [2]. PF-2341066 potently inhibited NPM-ALK phosphorylation in Karpas299 or SU-DHL-1 ALCL cells (IC50: 24 nmol/L). PF-2341066 potently inhibited cell proliferation, which was associated with G(1)-S-phase cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis in ALK-positive ALCL cells (IC50: 30 nmol/L) but not ALK-negative lymphoma cells. The induction of apoptosis was confirmed using terminal deoxyribonucleotide transferase-mediated nick-end labeling and Annexin V staining (IC50: 25-50 nmol/L) [3]. |
| In vivo | PF-2341066 showed efficacy at well-tolerated doses, including marked cytoreductive antitumor activity, in several tumor models that expressed activated c-Met. The antitumor efficacy of PF-2341066 was dose-dependent and showed a strong correlation to the inhibition of c-Met phosphorylation in vivo. Near-maximal inhibition of c-Met activity for the full dosing interval was necessary to maximize the efficacy of PF-2341066. Additional mechanism-of-action studies showed a dose-dependent inhibition of c-Met-dependent signal transduction, tumor cell proliferation (Ki67), induction of apoptosis (caspase-3), and reduction of microvessel density (CD31) [1]. Treatment of c-MET-amplified GTL-16 xenografts with 50 mg/kg crizotinib caused tumor regression that was associated with a slow reduction in (18)F-FDG uptake and reduced expression of the GLUT-1. Although baseline (18)F-FDG uptake into U87MG tumors was substantially higher than in GTL-16 tumors, (18)F-FDG uptake into U87MG tumors remained unchanged on treatment at 50 mg/kg crizotinib, despite tumor growth inhibition of 93% on day 8 of treatment [4]. |
| Kinase Assay | c-Met catalytic activity was quantitated using a continuous-coupled spectrophotometric assay in which the time-dependent production of ADP by c-Met was determined by analysis of the rate of consumption of NADH. NADH consumption was measured by a decrease in absorbance at 340 nm by spectrophotometry at designated time points. To determine Ki values, PF-2341066 was introduced into test wells at various concentrations in the presence of assay reagents and incubated for 10 min at 37°C. The assay was initiated by the addition of the c-Met enzyme [1]. |
| Cell Research | Cells were seeded in 96-well plates in media supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and transferred to serum-free media (with 0.04% BSA) after 24 h. In experiments investigating ligand-dependent RTK phosphorylation, corresponding growth factors were added for up to 20 min. After incubation of cells with PF-2341066 for 1 h and/or appropriate ligands for the designated times, cells were washed once with HBSS supplemented with 1 mmol/L Na3VO4, and protein lysates were generated from cells. Subsequently, phosphorylation of selected protein kinases was assessed by a sandwich ELISA method using specific capture antibodies used to coat 96-well plates and a detection antibody specific for phosphorylated tyrosine residues. Antibody-coated plates were (a) incubated in the presence of protein lysates at 4°C overnight; (b) washed seven times in 1% Tween 20 in PBS; (c) incubated in a horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti–total-phosphotyrosine (PY-20) antibody (1:500) for 30 min; (d) washed seven times again; (e) incubated in 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine peroxidase substrate to initiate a colorimetric reaction that was stopped by adding 0.09 N H2SO4; and (f) measured for absorbance in 450 nm using a spectrophotometer [1]. |
| Animal Research | Daily treatment with PF-2341066 given in water by oral gavage was initiated when tumors were 100 to 600 mm^3 in volume. Tumor volume was determined by measurement with electronic Vernier calipers, and tumor volume was calculated as the product of its length × width2 × 0.4. Tumor volume was expressed on indicated days as the median tumor volume ± SE indicated for groups of mice. Percent (%) inhibition values were measured on the final day of study for drug-treated compared with vehicle-treated mice and are calculated as 100 × {1?[(TreatedFinal day ? TreatedDay 1)/(ControlFinal day ? ControlDay 1)]}. Tumor regression values were determined by calculating the ratio of median tumor volumes at the time when treatment was initiated to the median tumor volume on the final day of study for a given treatment group. Significant differences between the treated versus the control groups (P ≤ 0.001) were determined using one-way ANOVA [1]. |
| Synonyms | PF-02341066 |
| Molecular Weight | 450.34 |
| Formula | C21H22Cl2FN5O |
| Cas No. | 877399-52-5 |
| Smiles | O([C@H](C)C1=C(Cl)C(F)=CC=C1Cl)C2=CC(C3=CN(N=C3)C4CCNCC4)=CN=C2N |
| Relative Density. | 1.475g/cm3 |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 34.5 mg/mL (76.61 mM), Sonication and heating are recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+90% Saline: 1 mg/mL (2.22 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.