Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

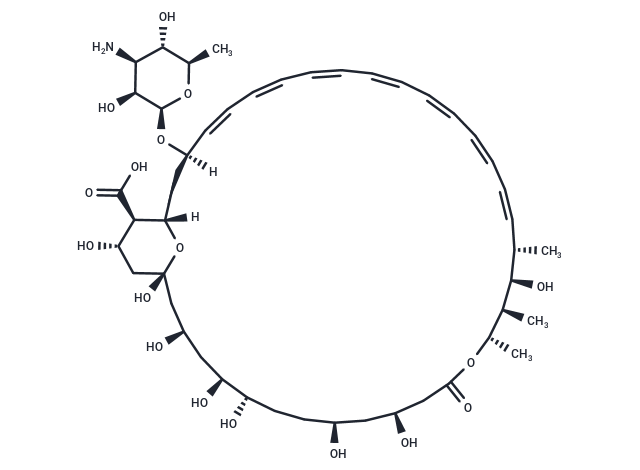
Amphotericin B (NSC-527017) is a polyene antifungal agent with broad-spectrum activity against many fungal species. Amphotericin B irreversibly binds to ergosterol and disrupts the integrity of cell membranes, resulting in antifungal activity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $31 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $44 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $76 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $98 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $32 | In Stock |
| Description | Amphotericin B (NSC-527017) is a polyene antifungal agent with broad-spectrum activity against many fungal species. Amphotericin B irreversibly binds to ergosterol and disrupts the integrity of cell membranes, resulting in antifungal activity. |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human normal colon epithelial cells CCD 841 CoTr and human colorectal cancer cells HT-29 were treated with Amphotericin B (0.05-25 µg/mL) for 24 h. Cell viability was measured by Neutral Red method. RESULTS: Higher concentrations of Amphotericin B were toxic to CCD 841 CoTr and HT-29 cells, with IC50 values of 8.7 µg/mL and 21.2 µg/mL, respectively. [1] METHODS: Candida albicans were treated with Amphotericin B (100 µM) for 4-16 min and imaged using the FLIM technique. RESULTS: Amphotericin B preferentially binds to the cell wall and does not efficiently cross the barrier covering the cell membrane.Amphotericin B can more readily pass through the cell wall barrier of young cells during the emergence stage. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To assay antifungal activity in vivo, Amphotericin B (0.25-4 mg/kg) was administered as a single intraperitoneal injection to C. albicans K-1-infected ICR/Swiss mice. RESULTS: Only the highest single dose of Amphotericin B treatment significantly reduced the number of colonies compared to the number of colonies at the start of treatment. [3] |
| Kinase Assay | THP-1 and HEK293 cells are transiently transfected using DEAE-dextran and Polyfect reagent, respectively. Plasmids transfected contain genes coding for the NF-κB-dependent pELAM-luc luciferase reporter, TLR2, TLR4, CD14, and MD2. Cells (5×105 THP-1 or 1×105 HEK293) are added to 12-well plates, washed after 18 h, and stimulated for 5 h. Cells are then lysed with reporter lysis buffer as directed, and lysates are analyzed for luminescence using Promega luciferase substrate and a Monolight 3010 luminometer. |
| Cell Research | Amphotericin B is dissolved in DMSO. The kinetics of cell death induced by AmB against Leishmania promastigotes is followed by using fluorometry with the DNA-binding compound ethidium bromide (EB). Fluorescence measurements are performed on a SPEX Fluorolog II spectrophotometer at 365-580 nm excitation-emission wavelengths. Promastigotes at a final concentration of 25×106 cells/mL are incubated for 5 min with gentle stirring in the fluorescence cuvette with 2 mL of different buffered solutions but always containing 10 mM glucose and EB (50 mM). After signal stabilization is achieved, AmB is added and dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide. Maximal EB incorporation is always obtained by adding digitonin (50 mg/mL). All solutions used are buffered with 75 mM TRIS (pH 4 7.6) and contain 150 mM NaCl (BNa+), 150 mM KCl (BK+), 150 mM choline chloride, and 100 mM sucrose, 100 mM NaCl. The osmolarity of all solutions is always adjusted to 390±5 mOsm using an advanced instrument SW2 osmometer. |
| Alias | NSC 527017 |
| Molecular Weight | 924.08 |
| Formula | C47H73NO17 |
| Cas No. | 1397-89-3 |
| Smiles | [H][C@]12C[C@@]([H])(O[C@@H]3O[C@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](N)[C@@H]3O)\C=C\C=C\C=C\C=C\C=C\C=C\C=C\[C@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](C)[C@H](C)OC(=O)C[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)CC[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)C[C@](O)(C[C@H](O)[C@H]1C(O)=O)O2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.34 g/cm3 |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 50 mg/mL (54.11 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 5 mg/mL (5.41 mM), Suspension. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.