Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Deferoxamine (Desferrioxamine B) is an iron chelator. Deferoxamine can be used to reduce the accumulation and deposition of iron in tissues. Deferoxamine can improve neurological dysfunction by inhibiting ferroptosis and neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury. It has antioxidant, anti-proliferation and anti-tumor activities, and can induce the production of HIF-1α, apoptosis and autophagy in cancer cells. It can be used to treat acute iron toxicity and COVID-19 related diseases.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $58 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $155 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $243 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $378 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $560 | - | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $809 | - | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $1,070 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $202 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Deferoxamine (Desferrioxamine B) is an iron chelator. Deferoxamine can be used to reduce the accumulation and deposition of iron in tissues. Deferoxamine can improve neurological dysfunction by inhibiting ferroptosis and neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury. It has antioxidant, anti-proliferation and anti-tumor activities, and can induce the production of HIF-1α, apoptosis and autophagy in cancer cells. It can be used to treat acute iron toxicity and COVID-19 related diseases. |
| Targets&IC50 | A2780 cells:3.5 μM, A549 cells:7.5 μM, DMS-53 cells:10 μM, HCT116 cells:> 200 μM |
| In vitro | METHODS: MEF cells were treated with Deferoxamine (1 mM) for 16 hours or 4 weeks, and the intracellular ROS level was detected. RESULTS: Deferoxamine reduces the ROS level in MEF cells. [1] METHODS: Human hepatoma cell line HepG was treated with Deferoxamine mesylate (100 μM) for 24 hours, and the proteins of InsR and p-Akt/total Akt/PKB were detected by wb. RESULTS: Deferoxamine enhances the expression and activity of InsR and induces an increase in p-Akt/total Akt/PKB levels. [2] METHODS: Tumor-associated MSCs and bone marrow MSCs were treated with Deferoxamine (5, 10, 25, 50, 100 μM) for 7 or 9 days to detect cell proliferation. RESULTS: Deferoxamine inhibits the proliferation of tumor-associated MSCs and bone marrow MSCs. [3] METHODS: Mesenchymal stem cells were treated with Deferoxamine (5, 10, 25, 50, 100 μM) for 7 days, and apoptosis was detected. RESULTS: Deferoxamine induces apoptosis of mesenchymal stem cells. [3] METHODS: Mesenchymal stem cells were treated with Deferoxamine (10 μM) for 3 days, and the expression of adhesion proteins in mesenchymal stem cells was detected by wb. RESULTS: Deferoxamine affects the expression of adhesion proteins in mesenchymal stem cells. [3] METHODS: SH-SY5Y cells were treated with Deferoxamine (100 μM) for 24 h, and the level of HIF-1α was detected by wb. RESULTS: Deferoxamine induces autophagy mediated by HIF-1α levels in SH-SY5Y cells. [4] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To study the role of Deferoxamine in wound healing in diabetes and the elderly, Deferoxamine was used to treat db/db mice (6.57 μg/ mouse; Drip infusion Once a day for 21 consecutive days. RESULTS: Deferoxamine can promote wound healing and increase new angiogenesis in elderly or diabetic mice. [1] METHODS: To study the effects of Deferoxamine on glucose uptake and insulin signaling, Deferoxamine was used to treat Sprague-Dawley rats (200 mg/kg; Intraperitoneal injection Once a day for two consecutive weeks. RESULTS: Deferoxamine can stabilize HIF-1α and increase glucose uptake, enhance the expression of InsR in the liver and signal transduction in vivo. [2] |
| Synonyms | Desferrioxamine B, Deferoxamine B |
| Molecular Weight | 560.68 |
| Formula | C25H48N6O8 |
| Cas No. | 70-51-9 |
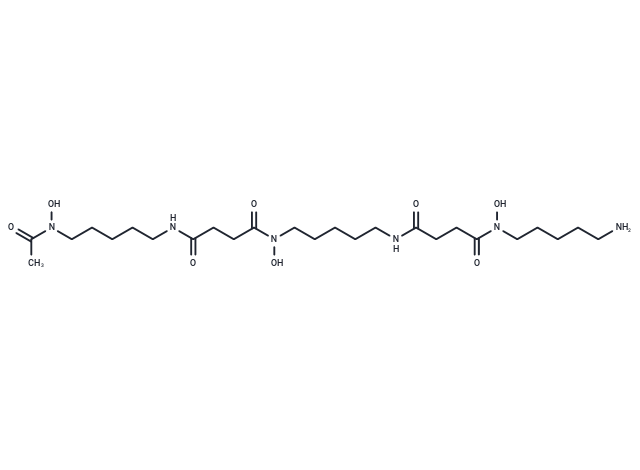
| Smiles | O=C(NCCCCCN(O)C(=O)C)CCC(=O)N(O)CCCCCNC(=O)CCC(=O)N(O)CCCCCN |
| Storage | store at low temperature | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 12.4 mg/mL (22.12 mM), Sonication and heating are recommended. H2O: 7.14 mg/mL (12.73 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 1 mg/mL (1.78 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.