 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Tolbutamide (HLS 831) is a sulphonylurea hypoglycemic agent with actions and uses similar to those of CHLORPROPAMIDE.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $41 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $59 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $45 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Tolbutamide (HLS 831) is a sulphonylurea hypoglycemic agent with actions and uses similar to those of CHLORPROPAMIDE. |
| Targets&IC50 | cAMP stimulated protein kinase:4 mM |
| In vitro | Daily treatment of cells with 450 mg/kg of Tolbutamide for seven consecutive days significantly increases the binding of insulin to adipocytes. The binding curve suggests an increase in the number of receptor sites rather than an increased affinity. This effect is associated with an enhanced insulin response in adipose tissue. Compared to the control group, adipocytes from Tolbutamide-treated animals show a notable increase in the conversion of glucose to fat in the presence of insulin. While low doses of Tolbutamide can elicit a metabolic effect by stimulating insulin secretion, they do not augment the number of insulin binding sites. An increase in insulin binding sites occurs only in the presence of high doses of Tolbutamide, which, at such levels, reduces overall insulin, including its pancreatic secretion and serum levels. |
| In vivo | Tolbutamide is effective only in patients who can normally produce insulin, as it helps to lower blood glucose levels. The compound inhibits the activity of both basal protein kinase and cyclic AMP-activated protein kinase, with an IC50 concentration of 4 mM. It dose-dependently inhibits the phosphorylation of bifunctional proteins induced by glucagon. In the presence of 10(-9) M glucagon, adding 2 mM Tolbutamide reduces the activity of 6-phosphofructokinase and enhances the activity of fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Additionally, Tolbutamide inhibits the activity of free and membrane-bound proteases in canine cardiac tissue. Its inhibitory effect on cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity in adipose tissue may account for its antilipolytic action. Tolbutamide also inhibits the proliferation of C6 glioma cells by increasing the concentration of Cx43, which is associated with reduced phosphorylation of pRb due to upregulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21 and p27. |
| Kinase Assay | cAMP kinase assay: Diced epididymal fat pads from fed Wistar rats (175-225 gm) are obtained after decapitation and incubated at 37 °C for two hours in Krebs-bicarbonate buffer containing 1.27 mM CaCl2. When added, Tolbutamide is present only during the incubation. After incubation fat pads are rinsed and sonicated in cold Krebs-bicarbonate buffer. The aqueous supematants from centrifugation at 50,000 × g for 30 minutes at 4 °C contained 0.75 to 1.25 mg protein per mL and are assayed for cyclic AMP-stimulated protein kinase activity. The assay is performed in 0.2 mL with these additions, 10 μmoles sodium glycerofiosphate pH 7.0, 2 μmoles sodium fluoride, 0.4 μmoles theophylline, 0.1 μmoles ethylene glyool bis (β-aminoethyl ether)-N, N'-tetraaoetic acid, 3 μmoles magnesium chloride, 0.3 mg mixed histone, 2 nmoles (γ- 32P) ATP, 1 nmoles cyclic AMP when indicated, and 0.05 ml of supernatant. |
| Cell Research | C6 glioma cells are incubated in serum-free DMEM at 37 °C for at least 24 hours before each experiment. Tolbutamide (400 μM) is incubated for 24 hours in serum-free medium. Incubations are performed at 37 °C in an atmosphere of 95% air/5% CO2 with 90–95% humidity. (Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | HLS 831 |
| Molecular Weight | 270.35 |
| Formula | C12H18N2O3S |
| Cas No. | 64-77-7 |
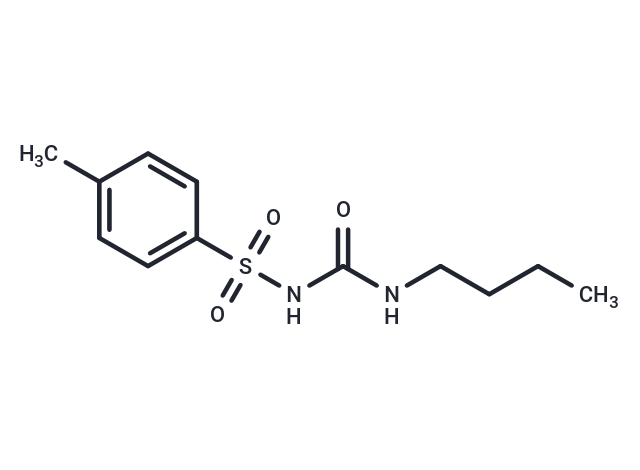
| Smiles | S(NC(NCCCC)=O)(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C)C=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.2450 g/cm3 |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 247.5 mg/mL (915.48 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 50 mg/mL (184.95 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (7.4 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.