Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

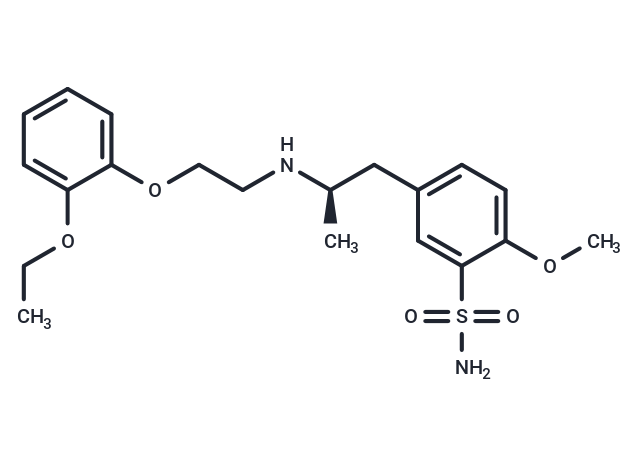
Tamsulosin ((R)-(-)-YM12617 free base) is an alpha1A adrenergic receptor antagonist used for the symptomatic treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It treats difficulty urinating, a common symptom of an enlarged prostate, by relaxing the neck muscles of the bladder and muscle fibers in the prostate itself, easing urination.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $48 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $68 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $98 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock |
| Description | Tamsulosin ((R)-(-)-YM12617 free base) is an alpha1A adrenergic receptor antagonist used for the symptomatic treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It treats difficulty urinating, a common symptom of an enlarged prostate, by relaxing the neck muscles of the bladder and muscle fibers in the prostate itself, easing urination. |
| Alias | LY253351 free base, HSDB-7744, HSDB7744, HSDB 7744, Harnal-D, Flowmax, (R)-(-)-YM12617 free base |
| Molecular Weight | 408.51 |
| Formula | C20H28N2O5S |
| Cas No. | 106133-20-4 |
| Smiles | CCOc1ccccc1OCCN[C@H](C)Cc1ccc(OC)c(c1)S(N)(=O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.191 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 90.0 mg/mL (220.3 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.