Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

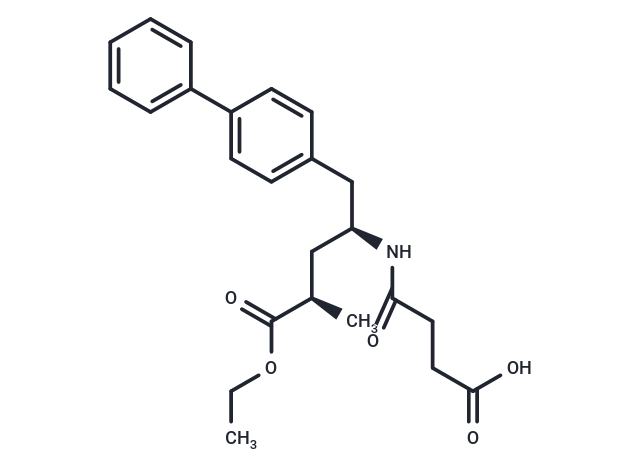
Sacubitril (AHU-377) is a potent NEP inhibitor with an IC50 of 5 nM and is a component of the heart failure medicine LCZ696.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $57 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $77 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $116 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $147 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $247 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $368 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $596 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $63 | In Stock |
| Description | Sacubitril (AHU-377) is a potent NEP inhibitor with an IC50 of 5 nM and is a component of the heart failure medicine LCZ696. |
| Targets&IC50 | NEP:5 nM |
| In vitro | LCZ696 is a single molecule that is comprised of molecular moieties of valsartan, an ARB, and Sacubitril, a neprilysin inhibitor (1:1 ratio). Sacubitril is converted by enzymatic cleavage of the ethyl ester into the active neprilysin inhibiting metabolite LBQ657[2]. The inactive NEPi precursor, Sacubitril, does not inhibit collagen accumulation in fibroblasts nor cardiac myocyte hypertrophy. In cardiac fibroblasts, the active NEPi LBQ657 had no discernible effects. In contrast, LBQ657 modestly inhibits cardiac myocyte hypertrophy[3]. |
| In vivo | In humans, Sacubitril (tmax0.5-1.1 h) are absorbed quickly. Sacubitril is converted rapidly into LBQ657 with its tmaxbeing reached in 1.9-3.5 h. Mean t1/2values for the biologically active LBQ657 is 9.9-11.1 h[2].In vehicle-treated dogs, ANF increases urinary sodium excretion from 17.3±3.6 to 199.5±18.4 pequivkglmin. This effect is potentiated significantly in animals which receive Sacubitril. Urinary volume is also potentiated in animals which receive an iv administration of Sacubitril[1]. |
| Alias | AHU-377, AHU377, AHU 377 |
| Molecular Weight | 411.49 |
| Formula | C24H29NO5 |
| Cas No. | 149709-62-6 |
| Smiles | CCOC(=O)[C@H](C)C[C@@H](Cc1ccc(cc1)-c1ccccc1)NC(=O)CCC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.151 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 27.5 mg/mL (66.83 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.