Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is a natural hormone-like substance involved in various physiological functions, including the contraction and relaxation of smooth muscles, dilation and constriction of blood vessels, regulation of blood pressure, and modulation of inflammation. It can be used to induce neuropathic pain models.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $42 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $65 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $89 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $179 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $256 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $370 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $543 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is a natural hormone-like substance involved in various physiological functions, including the contraction and relaxation of smooth muscles, dilation and constriction of blood vessels, regulation of blood pressure, and modulation of inflammation. It can be used to induce neuropathic pain models. |
| Targets&IC50 | EP2 receptor (NPEC cells):67 nM (EC50), EP1 receptor:74.4 nM (EC50), EP3 receptor:5.4 nM (EC50), EP4 receptor:7.1 nM (EC50) |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human colorectal cancer cells LS-174T were treated with Prostaglandin E2 (0.05-10 μM) for 1-60 min, and the expression levels of target proteins were detected by Western Blot. RESULTS: Prostaglandin E2 induced phosphorylation of Akt as early as 1 min after stimulation, and the activation of Akt reached a maximum within 10 min and persisted until 60 min. The addition of Prostaglandin E2 activated Akt in a dose-dependent manner. [1] METHODS: FDC-like cells were treated with Prostaglandin E2 (1 μM) for 15-120 min, and the expression levels of target proteins were detected by Western Blot. RESULTS: Prostaglandin E2 did not increase p-ERK, but decreased p-ERK at 60 and 120 min. on the contrary, p-p38 increased starting at 15 min and continued to 60 min. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To test the role of EP2 receptors in the in vivo absorption response, Prostaglandin E2 (3 mg/kg) was injected subcutaneously four times daily for three days into EP2+/+ and EP2-/- mice on a 129/SvEv background. RESULTS: Prostaglandin E2 increased serum calcium from 9.8+/-0.5 to 10.7+/-0.3 mg/dL in EP2+/+ mice but not in EP2-/- mice. [3] METHODS: To study the effects on bone, Prostaglandin E2 (6 mg/kg) was injected subcutaneously into C57BL/6 mice once daily for 3-12 days. RESULTS: Prostaglandin E2-treated mice showed a decrease in trabecular bone volume (BV/TV) at 14 days, indicating increased bone resorption. However, the Prostaglandin E2-treated 3-day group also stimulated bone formation at 14 days due to increased mineral deposition rate (MAR) and bone formation rate (BFR/BS). [4] |
| Synonyms | Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), PGE2, Dinoprostone |
| Molecular Weight | 352.47 |
| Formula | C20H32O5 |
| Cas No. | 363-24-6 |
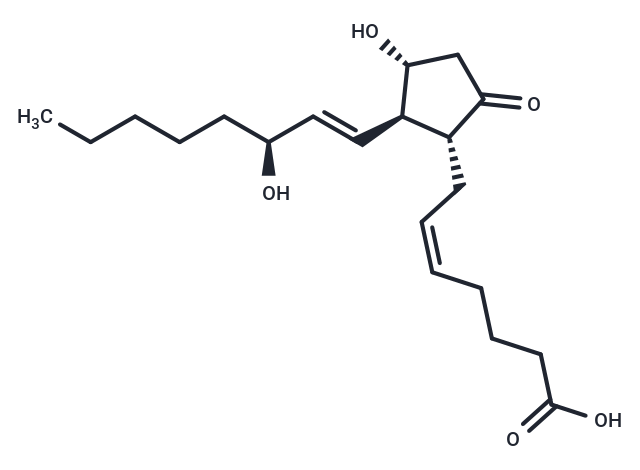
| Smiles | CCCCC[C@H](O)\C=C\[C@H]1[C@H](O)CC(=O)[C@@H]1C\C=C/CCCC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.148 g/cm3 |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 250 mg/mL (709.28 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 5% DMSO+95% Saline: 1.5 mg/mL (4.26 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.