Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
PMSF (Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride) is an irreversible inhibitor of serine/cysteine protease and is often used in the preparation of cell lysates.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $33 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $46 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $55 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | PMSF (Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride) is an irreversible inhibitor of serine/cysteine protease and is often used in the preparation of cell lysates. |
| Targets&IC50 | hypothermia (mouse):224 mg/kg (ED50), Neutrophil:95 μM, Neutrophil:130.9 μM, Neutrophil:22.8 μg/mL, Remain immobile (mouse):206 mg/kg (ED50), antinociception (mouse):86 mg/kg (ED50) |
| In vitro | Treatment with PMSF (intraperitoneal injection) in mice elicits cannabinoid-like effects, providing analgesia (ED50: 86 mg/kg), hypothermia (ED50: 224 mg/kg), and catalepsy (ED50: 206 mg/kg). When administered to Sprague-Dawley rats, PMSF induces a dose-dependent analgesic effect and significantly potentiates the analgesic effect of β-endorphin in vivo. By inhibiting fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity, PMSF suppresses typical cannabinoid or Δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol-like effects in ICR mice. Pretreatment with 30 mg/kg PMSF before the injection of [3H]-labeled cannabinoids results in a notable increase in brain cannabinoid levels after 5 minutes compared to [3H]-THC. PMSF pretreatment at 30 mg/kg enhances the cannabinoid-induced effects on the tail-flick response (analgesic effect), locomotion, and spontaneous activity by 5, 8, and 10-fold respectively. Administering PMSF 12 hours before paraoxon (PSP) protects hens from delayed neurotoxicity, whereas administration 4 hours later exacerbates the neurotoxic effects. PMSF pretreatment also prevents organophosphate-induced delayed neuropathy in hens and inhibits neuropathilament degeneration induced by tri-ortho-tolyl phosphate. |
| In vivo | METHODS: To study the analgesic effect of PMSF, PMSF was intraperitoneally injected into mice. RESULTS: Mice exhibited cannabinoid effects: including analgesia, hypothermia and immobility, with ED50 values of 86, 224 and 206 mg/kg, respectively. |
| Synonyms | Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, Benzylsulfonyl fluoride |
| Molecular Weight | 174.19 |
| Formula | C7H7FO2S |
| Cas No. | 329-98-6 |
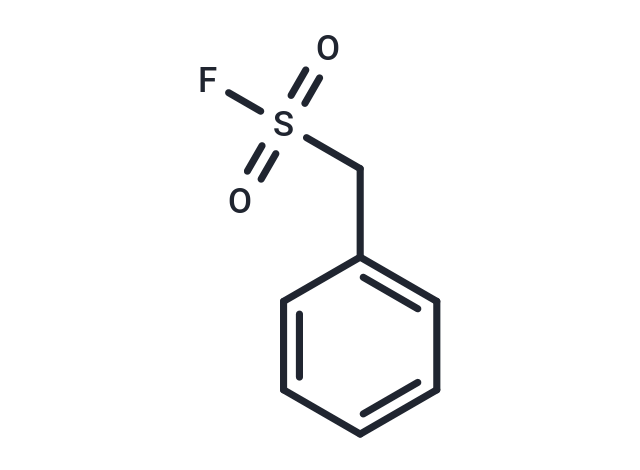
| Smiles | FS(=O)(=O)Cc1ccccc1 |
| Relative Density. | 0.797g/mLat 20°C |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 17.4 mg/mL (99.89 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 257.5 mg/mL (1478.27 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 5 mg/mL (28.7 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.