Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
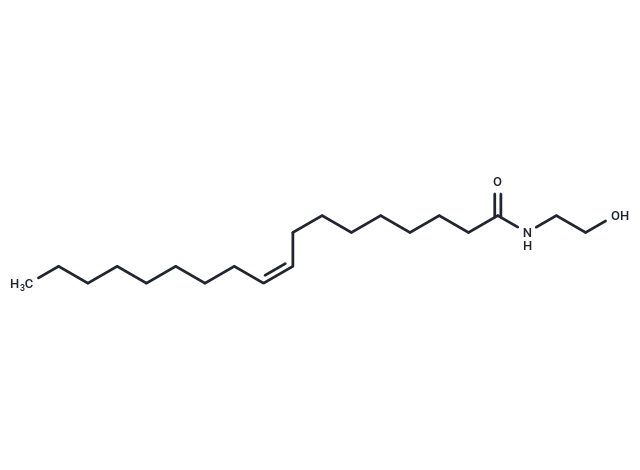
Oleoylethanolamide (N-Oleoylethanolamide) is a high affinity endogenous agonist of PPAR-α.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $73 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $148 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $263 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $396 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $579 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $53 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Oleoylethanolamide (N-Oleoylethanolamide) is a high affinity endogenous agonist of PPAR-α. |
| In vitro | In vitro studies showed that OEA inhibited transforming growth factor β1-stimulated HSCs activation through suppressing Smad2/3 phosphorylation, α-SMA expression and myofibroblast transformation. |
| In vivo | Treatment with OEA (5 mg/kg/day, intraperitoneal injection, i.p.) significantly attenuated the progress of liver fibrosis in both two experimental animal models by blocking the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs).?Gene expression analysis of hepatic tissues indicated that OEA inhibited the expression of α-smooth muscle action (α-SMA) and collagen matrix, fibrosis markers, and genes involved in inflammation and extracellular matrix remodeling. |
| Synonyms | Oleic acid monoethanolamide, Oleamide MEA, N-Oleoylethanolamide |
| Molecular Weight | 325.53 |
| Formula | C20H39NO2 |
| Cas No. | 111-58-0 |
| Smiles | CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)NCCO |
| Relative Density. | 0.915 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) DMSO: 250 mg/mL (767.98 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (6.14 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.