Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Nefiracetam (DM9384) are underway in Phase 2 trials. Nefiracetam, a GABAergic, cholinergic,and monoaminergic neuronal system enhancer, is used for Ro 5-4864-induced convulsions.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $35 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $47 | In Stock | - | |
| 500 mg | $76 | In Stock | - | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Nefiracetam (DM9384) are underway in Phase 2 trials. Nefiracetam, a GABAergic, cholinergic,and monoaminergic neuronal system enhancer, is used for Ro 5-4864-induced convulsions. |
| In vitro | In DDY mice, Nefiracetam (>10 mg/kg) effectively inhibits convulsions induced by Ro 5-4864. Oral administration of Nefiracetam suppresses Ro 5-4864-induced seizures in EL mice. Administering Nefiracetam (1 time/day) prior to each training session facilitates the acquisition of avoidance responses. |
| In vivo | Nefiracetam, at low concentrations (0.01–0.1 μM), induces a transient inhibition of Ach-evoked currents, while at higher concentrations (1–10 μM), it provides a sustained enhancement of these currents. Specifically, 1 μM Nefiracetam doubles the long-lasting component of the calcium channel current without affecting the transient component. After a 10-minute treatment with Nefiracetam, Ach-induced current is reduced to 30% at 0.01 μM and 38% at 0.1 μM of the control levels. The compound interacts with the PKC pathway, augmenting the activity of nicotinic Ach receptors, thereby increasing the release of presynaptic glutamate, and leading to potentiation of synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. This mechanism may underlie cognitive enhancement elicited by Nefiracetam through its interaction with PKA and PKC pathways. In primary cultures of rat hippocampal neurons, Nefiracetam increases the ratio of nicotinic-sensitive excitatory postsynaptic currents. Moreover, in rat hippocampal slices in both the CA1 region and the dentate gyrus, Nefiracetam induces long-lasting synaptic potentiation, which can be inhibited by α-bungarotoxin and mecamylamine. |
| Kinase Assay | Assay of glutamate released: Hippocampal slices (400 μM) are prepared from the guinea pig brain using standard techniques. A slice is fixed on a pair of silver wire electrodes (10 Hz, 5 V, 0.1 ms in duration) at 1-minutes intervals for 10 minutes and submerged in 1 mL standard artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) (in mM: 125 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 1.24 mM KH2PO4, 1.3 mM MgSO4, 2 mM CaCl2, 26 mM NaHCO3, and 10 mM glucose) oxygenated with 95% O2 and 5% CO2 at 36 °C in the presence and absence of tetrodotoxin (TTX) (0.5 μM). In a different set of experiments, electrical stimulation is applied to slices treated with Nefiracetam (1 μM) in the presence and absence of α-bungarotoxin (50 nM) or mecamylamine (3 μM). A 100 μL aliquot of the medium filtered with millipore filters (0.45 μM) is injected onto the cation-exchanger column of the autoanalyser to separate amino acids and the amount of glutamate released is calculated using known amino acid standard concentrations. |
| Cell Research | The injected oocytes are transferred to the recording chamber 24 to 48 hours after incubation and continuously superfused at room temperature (20 to 22 °C) in a standard frog Ringer's solution (115 mM NaCl, 2 mM KCl, 1.8 mM CaCl2, and 5 mM HEPES, pH 7.0). Ca2+ -free extracellular solution consisted of 115 mM NaCl, 2 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 5 mM HEPES, and 1 mM EGTA, pH 7.0. To remove the effect of the muscarinic ACh receptor, 1 μM atropine is added to the extracellular solution. ACh-activated currents are recorded using two-electrode, voltage-clamp techniques. The currents are analyzed on a microcomputer using pClamp software. ACh is bath-applied to oocytes. Nefiracetam is dissolved in distilled water at 1 mM for stock solution and diluted into concentrations required with the extracellular solution. (Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | DZL-221, DM9384 |
| Molecular Weight | 246.3 |
| Formula | C14H18N2O2 |
| Cas No. | 77191-36-7 |
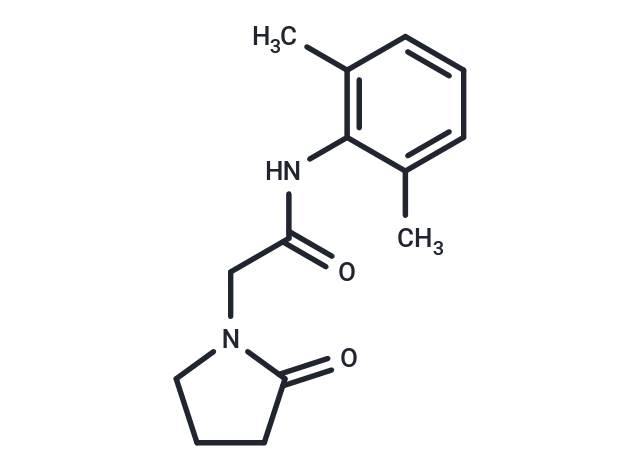
| Smiles | N(C(CN1C(=O)CCC1)=O)C2=C(C)C=CC=C2C |
| Relative Density. | 1.187 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 70 mg/mL (284.21 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 24.6 mg/mL (99.88 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (8.12 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.