Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Lamotrigine (BW430C) is an Anti-epileptic Agent and Mood Stabilizer. The physiologic effect of lamotrigine is by means of Decreased Central Nervous System Disorganized Electrical Activity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg | $31 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $46 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $72 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $48 | In Stock |
| Description | Lamotrigine (BW430C) is an Anti-epileptic Agent and Mood Stabilizer. The physiologic effect of lamotrigine is by means of Decreased Central Nervous System Disorganized Electrical Activity. |
| Targets&IC50 | 5-HT (human platelets):240 μM, 5-HT (rat brain synaptosomes):474 μM |
| In vitro | Lamotrigine is active in electrically induced EEG after-discharge tests, indicating its ability to counteract simple and complex partial seizures. It demonstrates antiepileptic effects in mice and rats, preventing hind-limb extension induced by both MES (maximal electroshock) and pentylenetetrazole. The peak effects of Lamotrigine occur 1 hour post-administration, with a duration exceeding 24 hours. Intravenous administration of Lamotrigine at doses greater than 5 mg/kg in rats results in a dose-dependent reduction in after-discharge duration. |
| In vivo | In rat cortical brain tissues cultured with 10 mg/L veratridine, Lamotrigine inhibited the release of glutamate and aspartate (both with an ED50 of 5.38 mg/L) twice as effectively as it inhibited the release of GABA (ED50 of 11.2 mg/L), without affecting the basal release of glutamate. Lamotrigine stabilizes presynaptic neuronal membranes by blocking voltage-dependent sodium channels, thereby preventing the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, especially glutamate and aspartate. It does not induce phencyclidine (PCP)-like central nervous system effects, does not act through direct inhibition of NMDA receptors, and may avoid the adverse effects associated with NMDA blockade. |
| Kinase Assay | Whole Cell [3H]R1881 Binding Assay: Fibroblasts are grown to confluence in five or six 150 cm2 tissue culture flasks for routine assay. This usually requires 4-6 weeks from the time of the initial seeding of the cell line. All studies are performed between passages 3-20. Two days before assay, the medium is changed to one lacking fetal calf serum. This is repeated again 24 hours before assay. Competition assays are performed with 0.5-1.0 nM [3H]R1881 and increasing amounts of the nonradioactive compounds. Binding to low affinity sites is determined in the presence of 5 × 10-7 M R1881 and is subtracted from whole cell binding of [3H]R 1881 obtained in the absence of any inhibitor to assess binding to 5 high affinity site |
| Alias | LTG, BW430C |
| Molecular Weight | 256.09 |
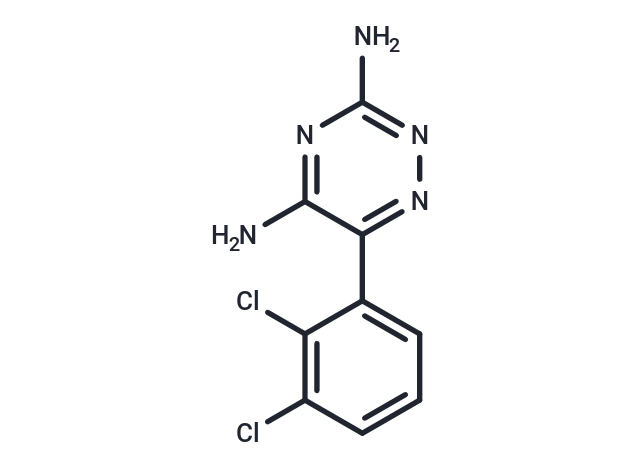
| Formula | C9H7Cl2N5 |
| Cas No. | 84057-84-1 |
| Smiles | NC1=NN=C(C(N)=N1)C1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1Cl |
| Relative Density. | 1.572 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 18.33 mg/mL (71.58 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 2.6 mg/mL (10.15 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.