 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Dorsomorphin (BML-275) is an AMPK inhibitor (Ki=109 nM) that is selective and ATP-competitive. Dorsomorphin inhibits the BMP type I receptors ALK2, ALK3, and ALK6. Dorsomorphin induces autophagy, and possesses antitumor activity.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $74 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $144 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $249 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $449 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $481 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Dorsomorphin (BML-275) is an AMPK inhibitor (Ki=109 nM) that is selective and ATP-competitive. Dorsomorphin inhibits the BMP type I receptors ALK2, ALK3, and ALK6. Dorsomorphin induces autophagy, and possesses antitumor activity. |
| Targets&IC50 | 92-1 cells:6.526 µM, HeLa cells:10.71 μM, Mel 270 cells:8.39 µM, A2780 cells:0.9 μM (EC50), AMPK:109 nM (Ki), MCF-7 cells:4.9 μM (EC50), OMM2.5 cells:31.45 µM, HCT116 cells:11.34 μM, MP46 cells:10.13 µM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human tumor cells HeLa and HCT116 were treated with Dorsomorphin (1.25-80 μM) for 24 h, and cell viability was measured by CCK-8. RESULTS: Dorsomorphin inhibited the viability of HeLa and HCT116 cells with IC50 values of 10.71 μM and 11.34 μM, respectively. [1] METHODS: ATL patient-derived PBMCs cells were treated with Dorsomorphin (5-25 μM) for 24 h. Apoptosis was detected by Flow Cytometry. RESULTS: Dorsomorphin increased the frequency of early apoptotic cells in PBMCs from patients with acute and chronic forms of ATL in a dose-dependent manner. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To test the antitumor activity in vivo, Dorsomorphin (10 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to NOD/SCID mice bearing human tumor S1T once daily for 28 days. RESULTS: Dorsomorphin inhibited the growth of human ATL tumor xenografts in NOD/SCID mice. [2] METHODS: To examine the effect on SMAD activity in vivo, Dorsomorphin (10 mg/kg) was administered as a single intraperitoneal injection to iron-dextran-treated C57BL/6 mice. RESULTS: Dorsomorphin eliminated iron-dextran-induced iron-mediated increase in hepatic SMAD1/5/8 phosphorylation. [3] |
| Kinase Assay | HT1080 cells are seeded in 24-well plates (2×104 cells per well) and treated with Dorsomorphin in the presence or absence of glucose or 10 mM 2DG for 2 h. HT1080 cells that overexpressed the wild-type and dominant negative AMPKα1 are prepared by transfecting plasmid DNA (pAMPKα1-wt, pAMPKα1-D168A and pcFlag as a control) in 6-well plates, seeding in 24-well plate and treating with UPR inhibitors. Cells are lysed with cell lysis buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 250 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 0.5% NP-40, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 0.2 mM PMSF, 1 μg/mL pepstatin, 0.5 μg/mL leupeptin, 5 mM NaF, 2 mM Na3Vo4, 2 mM β-glycerophosphate, 1 mM DTT). Relative AMPK kinase activity (mean±SD of duplicate determinations) to control sample (vehicle or pcFlag under normal growth conditions) is determined using the CycLex AMPK kinase assay kit[2]. |
| Cell Research | Dorsomorphin is dissolved in DMSO (10 mM) and stored,and then diluted with appropriate media (DMSO 0.5%) before use[2].HeLa and 786-O cells are treated with various concentrations of Dorsomorphin (0,0.3,1,3,10 μM ),Versipelostatin and Phenformin in the presence or absence of 10 mM 2DG or 1 μg/mL of Tunicamycin as a stressor for 30 h in 96-well plates.For the combination study,786-O cells are treated with various concentrations of UPR inhibitors in the presence or absence of 10 mM 2DG for 24 h.The medium is then replaced with fresh growth medium,and cells are cultured for a further 15 h.Subsequently,MTT is added to the culture medium,and the absorbance of each well is determined.For the viability assay under glucose-withdrawal conditions,HT1080 cells are treated with various concentrations of Dorsomorphin and phenformin in 12-well plates in the presence or absence of glucose for 18 h,seeded in 96-well plates with growth medium,and then cultured for a further 48 h before MTT is added.Relative cell survival (mean±SD of quadruplicate determinations) is calculated by setting each control absorbance from untreated cells as 100%.The effects of drug combinations at concentrations producing 80% cell growth inhibition (IC80) are analyzed using the isobologram method[2]. |
| Synonyms | Compound C, BML-275 |
| Molecular Weight | 399.49 |
| Formula | C24H25N5O |
| Cas No. | 866405-64-3 |
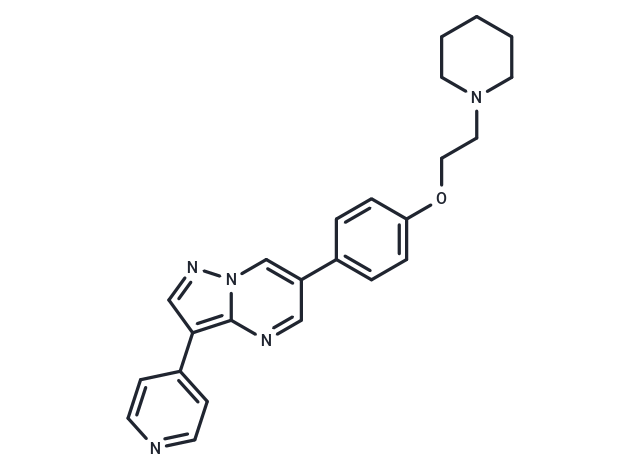
| Smiles | C(CN1CCCCC1)Oc1ccc(cc1)-c1cnc2c(cnn2c1)-c1ccncc1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.255g/cm3 |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 1.33 mg/mL (3.33 mM), Sonication and heating are recommended. 1M HCI: 255 mg/mL (638.31 mM) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+90% Saline: 0.13 mg/mL (0.33 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/1M HCI
1M HCI
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.