 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Curcumin (Natural Yellow 3) is a phenolic natural product, an inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase p300/CREB (IC50=25 μM) with specificity. Curcumin has a wide range of pharmacological activities such as antitumor, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $37 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $50 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $86 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $118 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $197 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Curcumin (Natural Yellow 3) is a phenolic natural product, an inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase p300/CREB (IC50=25 μM) with specificity. Curcumin has a wide range of pharmacological activities such as antitumor, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant. |
| Targets&IC50 | LoVo cells viability:20 ± 0.05 µM, p300 HAT:25 μM, HCT116 cells viability:10 ± 0.03 µM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Retinoblastoma cells SO-Rb50 and Y79 were treated with Curcumin (10-50 μM) for 24 h. Cell viability was measured by CCK-8. RESULTS: Curcumin dose-dependently and significantly decreased the cell viability of SO-Rb50 and Y79 cells, with IC50s of 38.4 μM and 34.8 μM, respectively.[1] METHODS: Mouse colon cancer cells MC38 were treated with Curcumin (5-50 μM) for 48 h. Apoptosis was detected by Flow Cytometry. RESULTS: Curcumin dose-dependently induced apoptosis in MC38 cells. [2] METHODS: Human pancreatic cancer cells PANC1 were treated with Curcumin (10-80 μg/mL) for 24 h. The autophagy marker LC3 was detected by Immunofluorescence. RESULTS: The highest expression level of punctate autophagosomes was found in 40 μg/mL Curcumin-treated cells. [3] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To detect the anti-tumor activity in vivo, Curcumin (100-200 mg/kg) was administered by gavage every three days for three weeks to C57BL/6J mice bearing mouse colon cancer tumor MC38. RESULTS: The average tumor volume and tumor weight of mice in the Curcumin treatment group were significantly reduced, and the tumor volume and tumor weight of the 200 mg/kg treatment group were also significantly lower than those of the 100 mg/kg treatment group. [2] METHODS: To detect anti-tumor activity in vivo, Curcumin (25-50 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally into BALB/c mice bearing Ehrlich ascites tumor EAT once daily for ten days. RESULTS: The number of EAT cells in the peripheral tissues of the Curcumin 50 mg/kg group was significantly less than that of the tumor control group. [4] |
| Cell Research | 1×104 B16-R cells are cultivated as monolayer culture for 12 hr. They were then incubated in 200 μL of RPMI, 10% FBS containing curcumin at final concentrations from 1–100 μM in 96-multiwell plates for 24-48 hr. After these incubations, cells are washed twice in PBS and 500 μl of fresh culture medium containing MTT (0.3 mg/mL) are added for colorimetric assay. (Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | Turmeric yellow, Natural Yellow 3, Indian Saffron, Diferuloylmethane |
| Molecular Weight | 368.38 |
| Formula | C21H20O6 |
| Cas No. | 458-37-7 |
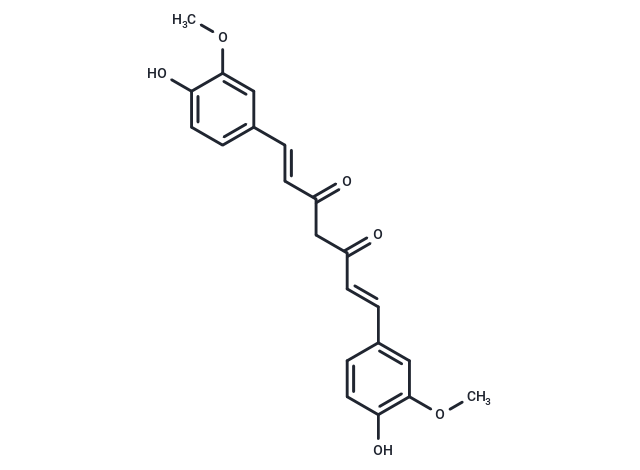
| Smiles | COC1=CC(\C=C\C(=O)CC(=O)\C=C\C2=CC(OC)=C(O)C=C2)=CC=C1O |
| Relative Density. | 0.93 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 265.00 mg/mL (719.37 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 1.80 mg/mL (4.89 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 6.00 mg/mL (16.29 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.