 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

COH29 (RNR Inhibitor COH29) is an orally available, aromatically substituted thiazole and human ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. COH29 binds to the ligand-binding pocket of the RNR M2 subunit (hRRM2) near the C-terminal tail, decreasing the pool of deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates needed for DNA synthesis, leading to cell cycle arrest and growth inhibition. It may also inhibit the nuclear enzyme poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) 1, preventing DNA repair, causing accumulation of DNA breaks, and inducing apoptosis.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $31 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $44 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $72 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $122 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $198 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $372 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $619 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $877 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $79 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | COH29 (RNR Inhibitor COH29) is an orally available, aromatically substituted thiazole and human ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. COH29 binds to the ligand-binding pocket of the RNR M2 subunit (hRRM2) near the C-terminal tail, decreasing the pool of deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates needed for DNA synthesis, leading to cell cycle arrest and growth inhibition. It may also inhibit the nuclear enzyme poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) 1, preventing DNA repair, causing accumulation of DNA breaks, and inducing apoptosis. |
| Targets&IC50 | RNR:16 μM. |
| In vitro | COH29 overcome gemcitabine and hydroxyurea resistance in Y cells. It potently inhibits proliferation of most cell lines in the NCI 60 human Y panel, most especially leukemia and ovarian Y, but exerts little effect on normal fibroblasts or endothelial cells. NMR, site-directed mutagenesis, and surface plasmon resonance biosensor studies confirm COH29 binding to the proposed ligand-binding pocket and offer evidence for assembly blockade of the RRM1-RRM2 quaternary structure[1]. |
| In vivo | COH29 (50/100 mg/kg, b.i.d., p.o.)results in a dose-dependent inhibition of MOLT-4 tumor xenograft growth, which is pronounced by Day 12 of treatment. In mice bearing TOV11D xenografts, 7 days of treatment with COH29 (200/300/400 mg/kg/day) results in a dose-dependent inhibition of tumor xenograft growth. Compared with the control group, tumor growth is significantly inhibited [1]. |
| Kinase Assay | For kinase assays following immunoprecipitation of FLAG-CDK7 protein from HCT116 or FLAG-CDK12 from 293A cellular lysates, cells are first treated with THZ1, THZ1-R, or DMSO for 4 hrs at 37°C. Cells are then harvested by lysis in 50 mM Tris HCl pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1% NP-40, 5 mM EDTA, and protease/phosphatase cocktails. Exogenous CDK7 or CDK12 proteins are immunoprecipitated from cellular lysates using FLAG antibody- conjugated agarose beads. Precipitated proteins are washed with lysis buffer 6 times, followed by 2 washes with kinase buffer (40 mM Hepes pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 5% glycerol) and subjected to in vitro kinase assays at 30°C for 45 minutes using 1 μg of the large subunit of RNAPII (RPB1) as substrate and 25 μM ATP and 10 μCi of 32P ATP. Kinase assays using recombinant CDK7/TFIIH/MAT1 are conducted in the manner as described above using 25 ng of CAK complex per reaction. For kinase assays designed to test time-dependent inactivation of CDK7 kinase activity, CAK complex is pre-incubated with indicated concentrations of THZ1, THZ1-R, or DMSO in kinase buffer without ATP for 4 hrs at 30°C prior to being subjected to kinase assay conditions[1]. |
| Cell Research | Cells is seeded into 96-well plates in 100 μL of complete medium at 2000 to 5000 cells per well, depending on the cell line's growth rate. After overnight incubation, test compound is added to each well at various concentrations in 50 μL of culture medium. After a further incubation for 96 hours at 37°C, fluorescein diacetate (final concentration: 10 mg/mL) and eosin Y [final concentration: 0.1% (w/v)] is added to each well, and the cells is incubated for an additional 20 minutes at 37°C. Cytotoxicity is assessed by Digital Imaging Microscopy System detection Viability is assessed using MTS [(3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium)] as previously described[1]. |
| Synonyms | RNR Inhibitor COH29 |
| Molecular Weight | 420.44 |
| Formula | C22H16N2O5S |
| Cas No. | 1190932-38-7 |
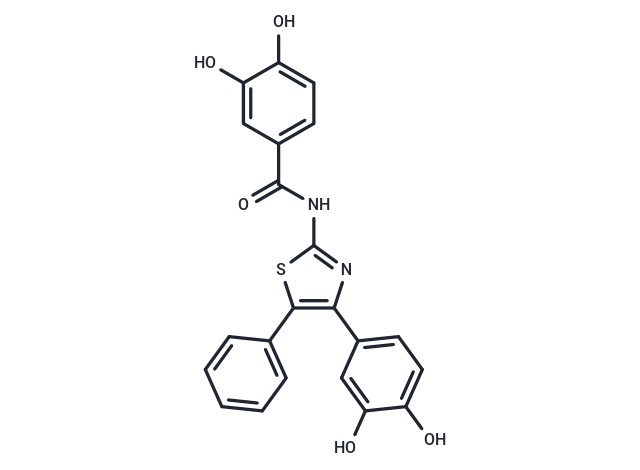
| Smiles | Oc1ccc(cc1O)C(=O)Nc1nc(c(s1)-c1ccccc1)-c1ccc(O)c(O)c1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (118.92 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (4.76 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.