 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

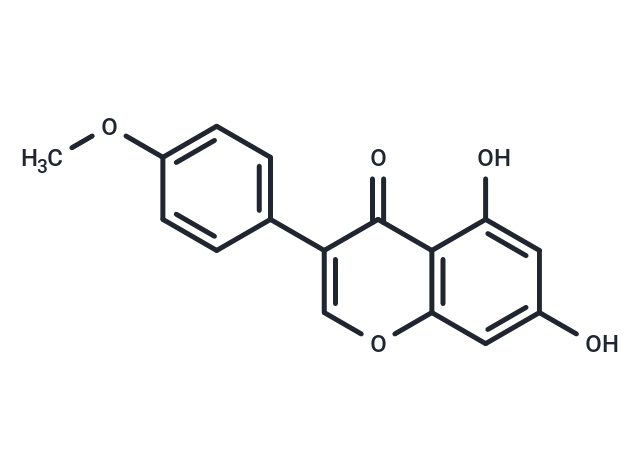
Biochanin A (4-Methylgenistein) is an isoflavone derivative isolated from red clover Trifolium pratense with anticarcinogenic properties. Biochanin A is a naturally occurring fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibitor.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $46 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $82 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Biochanin A (4-Methylgenistein) is an isoflavone derivative isolated from red clover Trifolium pratense with anticarcinogenic properties. Biochanin A is a naturally occurring fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibitor. |
| Targets&IC50 | EGFR:91.5 μM, FAAH (mouse):1.8 μM, FAAH (human):2.4 μM, FAAH (rat):1.4 μM |
| In vivo | LD50: Mice 63 mg/kg (i.p.) [4] |
| Kinase Assay | For experiments with FAAH, rat liver homogenates, mouse brain homogenates and membranes from COS7 cells transfected with the human enzyme are used. Frozen (?80°C) livers from adult C57BL/6 mice and frozen brains (minus cerebella) from adult Wistar or Sprague-Dawley rats are thawed and homogenized in 20 mM HEPES, 1 mM MgCl2, pH 7. The homogenates are centrifuged at ~35000×g for 20 min at 4°C. After resuspension in buffer followed by recentrifugation and a second resuspension in buffer, the pellets are incubated at 37°C for 15 min. This incubation is undertaken in order to hydrolyse all endogenous FAAH substrates. The homogenates are then centrifuged as above, recentrifuged and resuspended in 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.4, containing 1 mM EDTA and 3 mM MgCl2. The homogenates are then frozen at ?80°C in aliquots until used for assay. FAAH is assayed in the homogenates and in the COS7 cell membranes using 0.5 μM (unless otherwise stated) [3H]AEA labelled in the ethanolamine part of the molecule. Blank values are obtained by the use of buffer rather than homogenate. In the experiments comparing effects of Biochanin A upon FAAH and FAAH-2, the same assay is used but with 16 nM [3H]oleoylethanolamide ([3H]OEA) as substrate and with an incubation phase at room temperature. The choice of OEA rather than AEA for FAAH-2 is motivated by the relative rates of hydrolysis: OEA is metabolized four times faster than AEA by FAAH-2, whereas for FAAH the rate of hydrolysis of OEA is about a third of that for AEA. When 0.5 μM [3H]AEA is used as substrate, assay conditions for rat brain and mouse liver are chosen so that <10% of added substrate is metabolized. For the human FAAH samples, <5% of the [3H]AEA is metabolized in all cases. For 16 nM [3H]OEA, a limited supply of an expensive ligand meant that optimization is not possible, and the amount of substrate utilized is higher (34±1 and 0.5±0.1% for FAAH and its corresponding mock-transfected, respectively; 40±2 and 21±0.4 for FAAH-2 and its corresponding mock-transfected respectively)[1]. |
| Synonyms | Olmelin, 4-Methylgenistein |
| Molecular Weight | 284.26 |
| Formula | C16H12O5 |
| Cas No. | 491-80-5 |
| Smiles | COC1=CC=C(C=C1)C1=COC2=C(C1=O)C(O)=CC(O)=C2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.42 g/cm3 |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 250 mg/mL (879.48 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 9 mg/mL (31.66 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (7.04 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.