 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

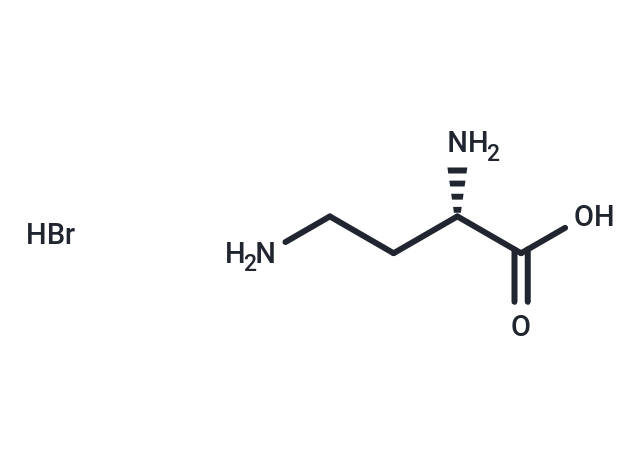
L-DABA hydrobromide (L-2,4-Diaminobutyric acid hydrobromide) is a potent GABA transaminase inhibitor with antitumor and anticonvulsant activity for the study of neurological disorders.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $41 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | L-DABA hydrobromide (L-2,4-Diaminobutyric acid hydrobromide) is a potent GABA transaminase inhibitor with antitumor and anticonvulsant activity for the study of neurological disorders. |
| In vitro | Incubation with 10 mM L-2,4-Diaminobutyric acid for 24 h at 37°C irreversibly and completely damages tumor cells. The cell-destructive effect caused by L-DABA hydrobromide is likely a result of osmotic lysis induced by the non-saturated intracellular accumulation of L-DABA hydrobromide. Concomitant incubation with L-alanine and L-methionine can abolish the harmful effect of L-DABA hydrobromide[1]. Kinetic studies indicate that L-DABA hydrobromide is a non-linear, non-competitive inhibitor of GABA transaminase activity. The elevation of GABA levels induced by L-DABA hydrobromide parallels the inhibition of GABA transaminase activity[2]. L-2,4-Diaminobutyric acid, an amino acid analogue, produces a cytolytic effect with a human glioma cell line, SKMG-1, and normal human fibroblasts. The concentrations of L-DABA hydrobromide necessary to reduce the cell count to 50% of control following a 24-h incubation at 37°C are 12.5 mM for the human fibroblasts and 20 mM for the glioma cell line[2]. |
| In vivo | Treatment with L-DABA hydrobromide leads to a 43.4% reduction in tumor growth[1]. In vivo, L-DABA hydrobromide more effectively inhibits GABA transaminase than it does in vitro[3]. |
| Synonyms | L-2,4-Diaminobutyric acid hydrobromide |
| Molecular Weight | 199.05 |
| Formula | C4H11BrN2O2 |
| Cas No. | 73143-97-2 |
| Smiles | Br.NCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O |
| Sequence | H-Dab-OH |
| Sequence Short | X |
| Storage | keep away from moisture | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 2 mg/mL (10.05 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.