Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
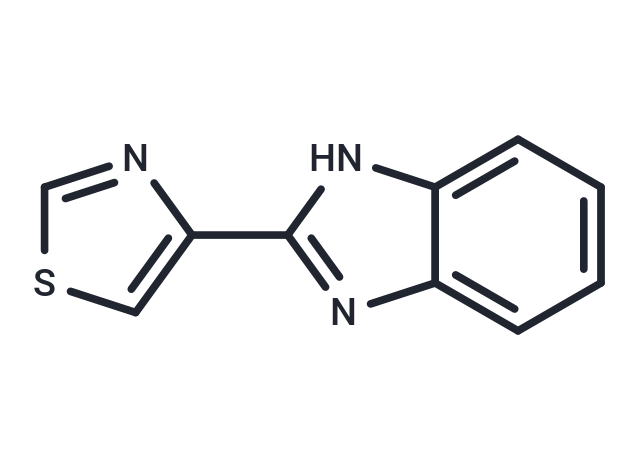
Thiabendazole (2-(4-Thiazolyl)benzimidazole) is a benzimidazole derivative with anthelminthic property.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $29 | In Stock | - | |
| 5 g | $40 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Thiabendazole (2-(4-Thiazolyl)benzimidazole) is a benzimidazole derivative with anthelminthic property. |
| Targets&IC50 | Proliferation (24 h, B16F10 cells):532.4 +/- 32.6 microM, Proliferation (48 h, B16F10 cells):322.9 +/- 28.9 microM, Proliferation (72 h, B16F10 cells):238.5 +/- 19.8 microM |
| In vitro | Thiabendazole provokes a strong DNA-damaging activity in the human lymphoblastoid cell line that constitutively expresses human CYP1A1 cDNA, but not in the parental line, indicating that CYP1A1 is chiefly implicated in carbaryl and thiabendazole genotoxicity. [1] Thiabendazole provokes a dose- and time-dependent increase in CYP1A1 (EROD activity, protein and mRNA levels) in primary culture of rat hepatocytes. [2] Thiabendazole results in the induction of 7-ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase and 7-pentoxyresorufin O-depentylase activities, CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP2B1 and CYP2B1/2 mRNA levels and CYP1A2 and CYP2B1/2 apoprotein levels. Thiabendazole markedly induces GSTP1 mRNA levels, but has only a small effect on GSTT1 mRNA levels. [3] Thiabendazole is rapidly transported by passive diffusion through the human intestinal cells by comparison with the protein-bound residues which are not able to cross the intestinal barrier. Thiabendazole will be firstly metabolized to 5OH-TBZ and subsequently converted to a chemically reactive metabolic intermediate binding to proteins. [4] |
| In vivo | Thiabendazole results in nephrosis or hydronephrosis and this organ toxicity may lead to the high dose-dependent mortality in treated mice. Thiabendazole results in hormone imbalance and this imbalance may play an important role in the changes of the reproductive or endocrine system in treated mice. [5] |
| Synonyms | 2-(4-Thiazolyl)benzimidazole |
| Molecular Weight | 201.25 |
| Formula | C10H7N3S |
| Cas No. | 148-79-8 |
| Smiles | N1C2=CC=CC=C2N=C1C1=CSC=N1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.406g/cm3 |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) Ethanol: 1 mg/mL (4.97 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 50 mg/mL (248.45 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 1 mg/mL (4.97 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.