Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

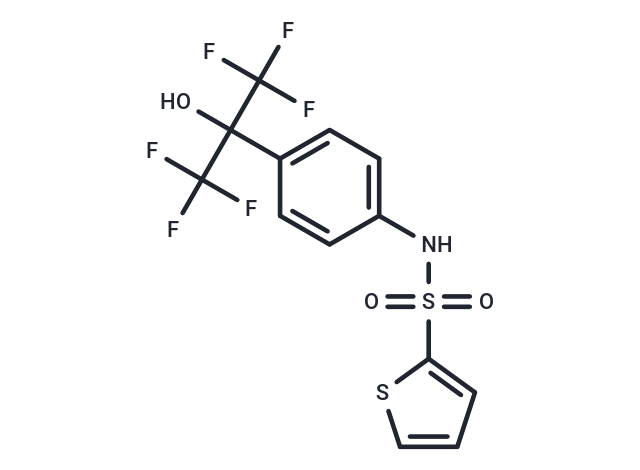
SR3335 (ML 176) is a selective inverse agonist of RORα that competitively inhibits the binding of 25-hydroxycholesterol to the ligand binding domain (Ki: 220 nM).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $31 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $72 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $128 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $258 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $478 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $689 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $79 | In Stock |
| Description | SR3335 (ML 176) is a selective inverse agonist of RORα that competitively inhibits the binding of 25-hydroxycholesterol to the ligand binding domain (Ki: 220 nM). |
| Targets&IC50 | RORα:220 nM(ki) |
| Alias | ML 176 |
| Molecular Weight | 405.34 |
| Formula | C13H9F6NO3S2 |
| Cas No. | 293753-05-6 |
| Smiles | OC(c1ccc(NS(=O)(=O)c2cccs2)cc1)(C(F)(F)F)C(F)(F)F |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 30 mg/mL (74.01 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 50 mg/mL (123.35 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.