Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Rafoxanide as a dual CDK4/6 inhibitor for the treatment of skin cancer. Rafoxanide is a salicylanilide used as an anthelmintic. It is used to treat fluke, hookworm and other infestations.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg | $31 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $75 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $48 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Rafoxanide as a dual CDK4/6 inhibitor for the treatment of skin cancer. Rafoxanide is a salicylanilide used as an anthelmintic. It is used to treat fluke, hookworm and other infestations. |
| In vitro | Rafoxanide exhibit a high cytotoxic effects (IC50: 1.09 μM for A375 and 1.31 μM for A431 cells).?Consistent with the expected properties of CDK4/6 inhibitors, rafoxanide significantly increased the G1 phase population.?Notably, Rafoxanide specifically decreased the expression of CDK4/6, cyclin D, retinoblastoma protein (Rb) and the phosphorylation of CDK4/6 and Rb[1]. |
| In vivo | Rafoxanide specifically decreased the expression of CDK4/6, cyclin D, retinoblastoma protein (Rb) and the phosphorylation of CDK4/6 and Rb. Furthermore, the anticancer effect of rafoxanide was demonstrated in vivo in BALB/C nude mice subcutaneously xenografted with human skin cancer A375 cells. Rafoxanide (40 mg/kg, i.p.) exhibited significant antitumor activity, comparable to that of oxaliplatin (5 mg/kg, i.p.). The combined administration of rafoxanide and oxaliplatin produced a synergistic therapeutic effect. First to indicate that rafoxanide inhibits CDK4/6 activity and is a potential candidate drug for the treatment of human skin cancer[1]. |
| Cell Research | Cell cycle analysis using an EPICS XL4 Flow Cytometer.?The cell cycle phase distribution was analyzed using ModFit LT 2.0 software.?Briefly, cells (4x10^4 ) were seeded in 24-well plates in DMEM containing 0.125% FBS.?After 24 h, the cell culture medium was replaced with DMEM containing 10% FBS and various doses of rafoxanide (1, 3, 10 or 30 μM) for 6, 12 or 24 h, as indicated.?At the end of the experiments, cells (1x10^4 ) were fixed in ice cold 70% ethanol, and stained using a Coulter DNA Prep Reagent kit , and cellular DNA content was assessed.?All data were obtained from two separate experiments performed in triplicate[1] |
| Animal Research | A375 cells (1x10^6 ) were suspended in 0.2 ml PBS, and injected subcutaneously into the right flank of the mice (n=3).?Tumor size was assessed using a caliper.?When the tumors grew to 80-100 mm^3 (1 week after inoculation), mice were divided randomly into different experimental groups (5 mice/group), and intraperitoneally injected daily for 21 days with various testing compounds(Rafoxanide).?The mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and the tumors were excised, weighed, and images were captured by camera .?The tumor volume was calculated using the formula V = ab^2 /2 (a = longest axis;?b = shortest axis)[1]. |
| Molecular Weight | 626.01 |
| Formula | C19H11Cl2I2NO3 |
| Cas No. | 22662-39-1 |
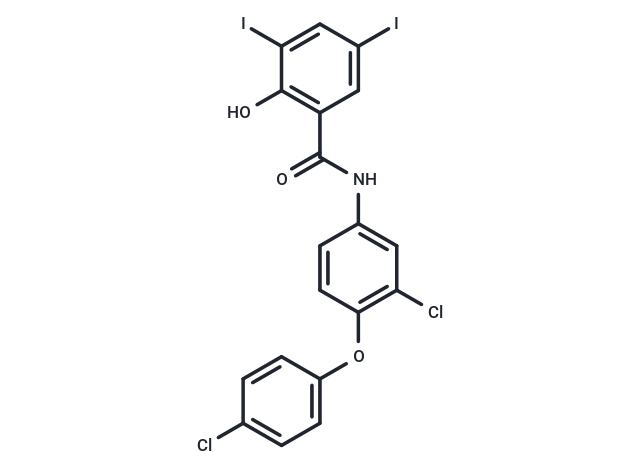
| Smiles | C(NC1=CC(Cl)=C(OC2=CC=C(Cl)C=C2)C=C1)(=O)C3=C(O)C(I)=CC(I)=C3 |
| Relative Density. | 2.05g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 6.27 mg/mL (10.02 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 1 mg/mL (1.6 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.