 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

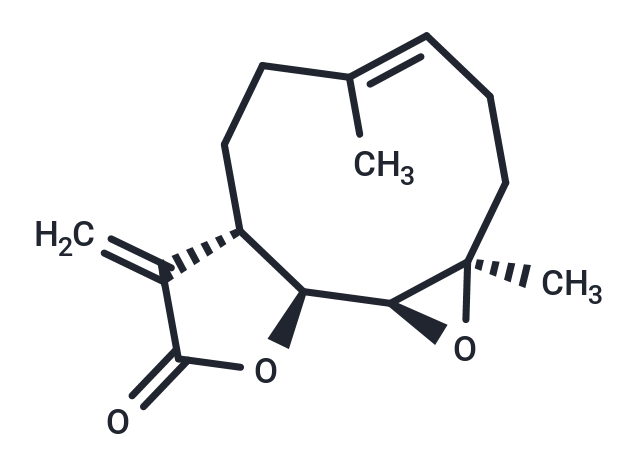
Parthenolide ((-)-Parthenolide) is a natural sesquiterpene lactone that is an NF-κB inhibitor and also specifically inhibits HDAC1 protein, but is inactive against other class I/II HDACs. Parthenolide has anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, and anti-viral activities.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $50 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $68 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $119 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Parthenolide ((-)-Parthenolide) is a natural sesquiterpene lactone that is an NF-κB inhibitor and also specifically inhibits HDAC1 protein, but is inactive against other class I/II HDACs. Parthenolide has anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, and anti-viral activities. |
| In vitro | Parthenolide (PTL) exhibits dose-dependent growth inhibition in NSCLC cells (Calu-1, H1792, A549, H1299, H157, H460) and induces apoptotic protein cleavage (CASP8, CASP9, CASP3, PARP1) in a concentration- and time-dependent manner, indicating apoptosis. Moreover, Parthenolide causes G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in A549 cells and G2/M arrest in H1792 cells in a concentration-dependent manner[2]. |
| In vivo | METHODS: To investigate the effects on metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), Parthenolide (2-6 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally three times per week for eight weeks to MAFLD model mice. RESULTS: Parthenolide exerted beneficial effects on hepatic injury, lipid metabolism, fibrosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress in mice with MAFLD, which were mediated by activation of the HIPPO pathway. [3] |
| Cell Research | Parthenolide (PTL) is dissolved in DMSO and diluted with appropriate media[2]. Cells are seeded in 96-well plates and treated on the second day with the given concentration of Parthenolide (0, 5, 10, 20 μM) for another 48 hours and then subjected to SRB or MTT assay. For SRB assay, live cell number is estimated as described earlier. After treatment, the medium is discarded firstly. In order to fix the adherent cells, 100 μL of cold trichloroacetic acid (10% (w/v)) are adding to each well and incubating at 4°C for at least 1 hour. The plates are then washed five times with deionized water and dried in the air. Each well are then added with 50 μL of SRB solution (0.4% w/v in 1% acetic acid) and incubated for 5 min at room temperature. The plates are washed five times with 1% acetic acid to remove unbound SRB and then air dried. The residual bound SRB is solubilized with 100 μL of 10 mM Tris base buffer (pH 10.5), and then read using a microtiter plate reader at 495 nm. The MTT assay is executed. 20 μL MTT (5 mg/mL) are added to each sample and incubate at 37°C for 4 h, then 100 μL solubilization solution are added. Cell viability is determined at 595 nm[2]. |
| Synonyms | (-)-Parthenolide |
| Molecular Weight | 248.32 |
| Formula | C15H20O3 |
| Cas No. | 20554-84-1 |
| Smiles | C\C1=C/CC[C@@]2(C)O[C@H]2[C@H]2OC(=O)C(=C)[C@@H]2CC1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.13 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 55 mg/mL (221.49 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 50 mg/mL (201.35 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 4.9 mg/mL (19.73 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.