 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Luminespib (VER-52296) is an HSP90 inhibitor that inhibits HSP90α and HSP90β (IC50=7.8/21 nM). Luminespib has antitumor activity and is used in studies of head and neck tumors, among others.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $52 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $74 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $148 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $233 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $382 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $569 | - | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $917 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $57 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Luminespib (VER-52296) is an HSP90 inhibitor that inhibits HSP90α and HSP90β (IC50=7.8/21 nM). Luminespib has antitumor activity and is used in studies of head and neck tumors, among others. |
| Targets&IC50 | GRP94:535 nM, HSP90 β:21 nM (cell free), TRAP1:85 nM, HSP90 α:7.8 nM (cell free) |
| In vitro | METHODS: H. pylori infected GES-1 cells were treated with Patchouli alcohol (5-20 µg/mL) for 24 h. Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry. RESULTS: Patchouli alcohol treatment significantly reduced H. pylori-induced apoptosis. [1] METHODS: H. pylori-infected GES-1 cells were treated with Patchouli alcohol (5-20 µg/mL) for 24 h. Cytokine levels were measured by ELISA. RESULTS: Treatment with 5-20 µg/mL Patchouli alcohol significantly reduced the production of TNF-α and MCP-1. [1] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To study the effect on H. pylori-associated gastritis, Patchouli alcohol (5-20 mg/kg) was administered orally to H. pylori infected mice once daily for two weeks. RESULTS: Patchouli alcohol treatment increased SH-NP content and CAT activity and significantly protected the gastric mucosa from H. pylori-induced damage. [1] |
| Cell Research | Cell lines were grown in DMEM/10% FCS, 2 mmol/L glutamine, and nonessential amino acids in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 in air. All lines were free of Mycoplasma. Cell proliferation was determined using the sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay for tumor cells and prostate epithelial cells, the WST-1 assay for MCF10A and HB119, or an alkaline phosphatase assay for HUVEC and HDMEC. GI50 was the compound concentration inhibiting cell proliferation by 50% compared with vehicle controls. Cell cycle analysis was as described. Active caspase-3/7 was measured using a homogenous caspase assay kit [1]. |
| Animal Research | In vivo, pharmacokinetic studies in female NCr athymic mice bearing WM266.4 human melanoma xenografts were essentially as described. NVP-AUY922 was dissolved in DMSO and diluted in sterile saline/Tween 20. A single dose of 50 mg/kg NVP-AUY922 was given i.v. or i.p. and groups of three animals were taken at intervals for pharmacokinetic analyses [1]. |
| Synonyms | VER-52296, NVP-AUY922, AUY922 |
| Molecular Weight | 465.54 |
| Formula | C26H31N3O5 |
| Cas No. | 747412-49-3 |
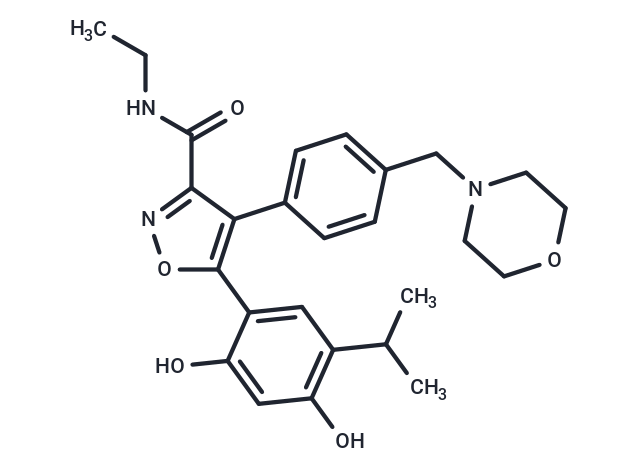
| Smiles | CCNC(=O)c1noc(c1-c1ccc(CN2CCOCC2)cc1)-c1cc(C(C)C)c(O)cc1O |
| Relative Density. | 1.234 g/cm3 |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 16.67 mg/mL (35.81 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 29 mg/mL (62.29 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 8.6 mg/mL (18.47 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/Ethanol
Ethanol
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.