Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Fusidic acid sodium salt (SQ-16360) is a sodium salt form of fusidic acid, a bacteriostatic antibiotic derived from the fungus Fusidium coccineum and used as a topical medication to treat skin infections.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $31 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $43 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $89 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $139 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $48 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Fusidic acid sodium salt (SQ-16360) is a sodium salt form of fusidic acid, a bacteriostatic antibiotic derived from the fungus Fusidium coccineum and used as a topical medication to treat skin infections. |
| In vivo | Fusidin(Fusidate Sodium) ameliorates EAM, at least partly, through an inhibitory action on the secretion of TNF-a[1]. It markedly attenuates clinical and histological signs of immunoinflammatory diabetes mellitus in mice given streptozotocin(SZ). The effect is dose-dependent, observed in three different strains of mice. Thus, fusidin might have an antidiabetogenic effect[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | Binding assays: Binding assays are performed as previously described (Allenby et al., 1993, 1994). Briefly, labeled and unlabeled retinoids are added to nucleosol or cytosolic fractions in ethanol so that the total amount of ethanol added is constant in all tubes and did not exceed 2% of the incubation volume. The receptor preparations are incubated with retinoids at 4°C for 4–6 hr. Sephadex PD-10 desalting columns are used to separate bound radioligand from free radioligand after equilib- rium is achieved. For competitive binding assays, varying concentrations of unlabeled competing ligand are incubated with the appropriate nucleosol or cytosol in the presence of a fixed concentration of [3H]tRA (sp. act. 49.3 Ci/mmol) or [3H]9-cis RA (sp. act. 24.0 Ci/mmol). Final concentrations of [3H] tRA and [3H]9-cis RA for nuclear receptor binding assays are 5 nM. Final concentrations of [3H] tRA for CRABP binding assays is 30 nM. The IC50s are calculated as described above (DeLean et al., 1978). For saturation kinetics, increasing concentrations of radiolabeled ligand ([3H]tRA sp. act. 49.3 Ci/mmol, [3H]TTNPB sp. act. 5.5 Ci/ mmol) are added to the nucleosol of the appropriate receptor subtype in the presence (nonspecific binding) or absence (total binding) of a 100-fold molar excess of the corresponding unlabeled retinoid. Specific binding is defined as the total binding minus nonspecific binding. Saturation kinetics are calculated as previously described (Scatchard, 1949; Grippo and Gudas, 1987; Levin et al., 1992). |
| Synonyms | SQ-16360, Sodium fusidate, Fusidate Sodium, Fucidin |
| Molecular Weight | 538.69 |
| Formula | C31H47NaO6 |
| Cas No. | 751-94-0 |
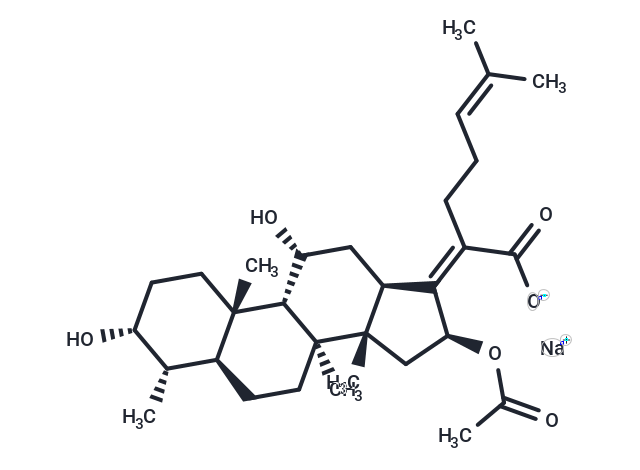
| Smiles | [C@]12([C@@]3([C@H](/C(=C(\CCC=C(C)C)/C(=O)[O-])/[C@H](C3)OC(=O)C)C[C@H]([C@H]1[C@@]1([C@@H](CC2)[C@@H]([C@@H](CC1)O)C)C)O)C)C.[Na+] |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 93 mg/mL (172.64 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 92 mg/mL (170.78 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 93 mg/mL (172.64 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 3.3 mg/mL (6.13 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.