 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Eprenetapopt (PRIMA-1Met) restores wild-type conformation and function to mutant p53, and triggers apoptosis in tumor cells. PRIMA-1MET also targets the selenoprotein thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1), a key regulator of cellular redox balance.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $67 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $107 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $217 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $387 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $687 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $1,390 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $74 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Eprenetapopt (PRIMA-1Met) restores wild-type conformation and function to mutant p53, and triggers apoptosis in tumor cells. PRIMA-1MET also targets the selenoprotein thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1), a key regulator of cellular redox balance. |
| Targets&IC50 | p53:, TrxR1: |
| In vitro | APR-246 inhibits both recombinant TrxR1 in vitro and TrxR1 in cells. Cellular TrxR1 activity is inhibited by APR-246 irrespective of p53 status. APR-246 can directly affect cellular redox status via targeting of TrxR1. Several small molecules have been shown to restore wild-type activity to mutant p53, including CP-31398, PRIMA-1 and APR-246 (PRIMA-1MET), MIRA, STIMA, PhiKan-083 and NSC319726. PRIMA-1 and its methylated analog APR-246 promote correct folding of mutant p53, induce cell death by apoptosis, and inhibit tumor growth in mice. APR-246 has also been shown to reactivate mutant forms of the p63 and p73 proteins that share high structural homology with p53. PRIMA-1MET is a powerful apoptosis-inducing agent. PRIMA-1MET can enhance apoptosis in mutant p53 carrying cells, compared to the p53 null parental cells. Most p53 mutants are in complex with Hsp70 proteins. PRIMA-1MET treatment increases Hsp70 expression and nucleolar translocation, in parallel with the induction of nucleolar accumulation of mutant p53. Several lines of evidence suggest that PRIMA-1MET can also act independently of the p53 status of the cell. It can radiosensitize prostate carcinoma cell lines with mutant or wild type p53 and p53-/- cells as well. Introduction of mutant p53 (p53ser249 or p53 gln248) into p53-/- hepatocarcinoma cells increases sensitivity to PRIMA-1MET without the induction of p53 target genes. PRIMA-1MET regularly induces apoptosis in mutant p53 expressing cells. |
| Kinase Assay | Cells are plated in six-well plates at a density of 15?000 cells per cm2. Next day, cells are treated with different concentrations of APR-246 (0, 25, 50, 75 and 100 μM) and harvested after 4, 12 and 24?h. The cells are lysed, and the clarified supernatants are used for either analysis of TrxR enzymatic activities or western blot. Total protein concentrations are determined with a Bradford reagent kit. Cellular TrxR activity is measured using an adapted Trx-dependent end point insulin reduction assay for microwell plates. |
| Synonyms | PRIMA-1Met, APR-246 |
| Molecular Weight | 199.25 |
| Formula | C10H17NO3 |
| Cas No. | 5291-32-7 |
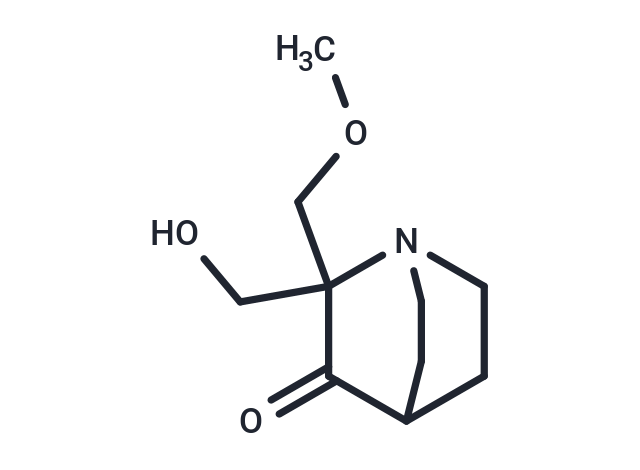
| Smiles | COCC1(CO)N2CCC(CC2)C1=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.20 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 100 mg/mL (501.88 mM) DMSO: 126.25 mg/mL (633.63 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (10.04 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.