Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
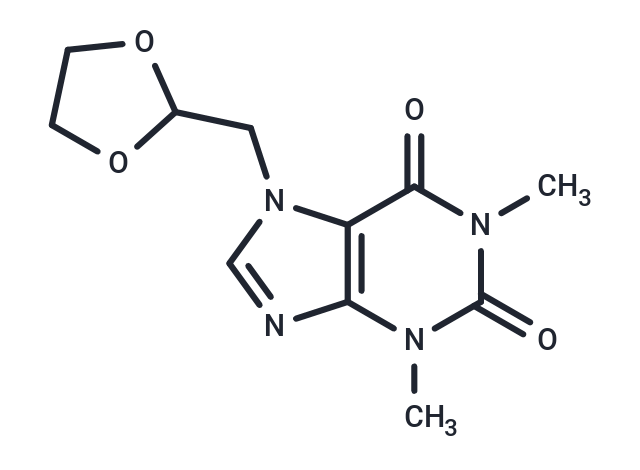
Doxofylline (Doxophylline) is a methylxanthine derivative with the presence of a dioxolane group in position 7. As a drug used in the treatment of asthma, doxofylline has shown similar efficacy to theophylline but with significantly fewer side effects in animal and human studies.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $33 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Doxofylline (Doxophylline) is a methylxanthine derivative with the presence of a dioxolane group in position 7. As a drug used in the treatment of asthma, doxofylline has shown similar efficacy to theophylline but with significantly fewer side effects in animal and human studies. |
| In vitro | At an effective therapeutic dose, Doxofylline exhibits a less pronounced cardiac stimulant effect compared to theophylline. As a result, Doxofylline does not significantly increase heart rate, nor does it induce arrhythmias. Administration of 30 mg/kg of Doxofylline results in an increase of 13 beats/min in the heart rate of anesthetized cats. |
| In vivo | Doxofylline exhibits the activity of a phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor and enhances the levels of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), thus it is utilized in the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Compared to theophylline, doxofylline significantly reduces the affinity for adenosine A1 and A2 receptors, which may contribute to its improved safety profile. Additionally, doxofylline does not interfere with calcium ion influx nor antagonize calcium channel blockers. In terms of inhibitory potency, the half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) of doxofylline against adenosine-induced tracheal smooth muscle relaxation is 15-fold higher than that of aminophylline, and it also displays a 15-fold higher EC50 in reducing the negative inotropic effect of adenosine on guinea pig atria than aminophylline. |
| Synonyms | Doxophylline |
| Molecular Weight | 266.25 |
| Formula | C11H14N4O4 |
| Cas No. | 69975-86-6 |
| Smiles | Cn1c2ncn(CC3OCCO3)c2c(=O)n(C)c1=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.59 g/cm3 |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (187.79 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 22 mg/mL (82.63 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 2 mg/mL (7.51 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (7.51 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/H2O/DMSO
H2O/DMSO
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.