Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
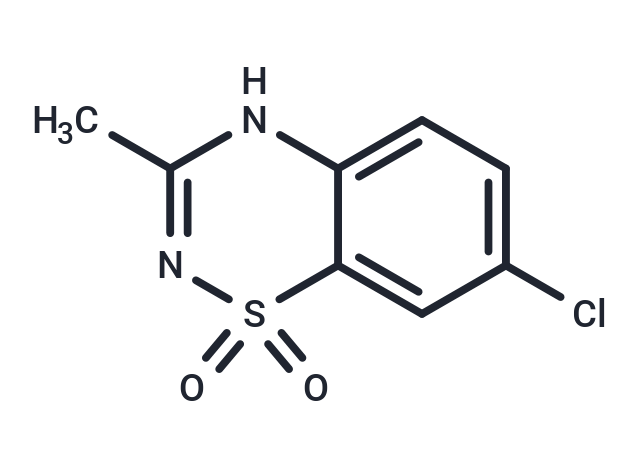
Diazoxide (Proglycem) is a benzothiadiazine derivative that is a peripheral vasodilator used for hypertensive emergencies. It lacks diuretic effect, apparently because it lacks a sulfonamide group.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $37 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $50 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $113 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $163 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Diazoxide (Proglycem) is a benzothiadiazine derivative that is a peripheral vasodilator used for hypertensive emergencies. It lacks diuretic effect, apparently because it lacks a sulfonamide group. |
| In vitro | Diazoxide inhibits microglial inflammatory activity. Diazoxide treatment partially inhibits the inflammatory pattern induced by LPS/IFN-γ in microglial cells, inducing a decrease in NO production that could be because of the decreased expression of iNOS detected. Diazoxide has no effect on microglial phagocytosis[1]. |
| In vivo | Diazoxide is beneficial on the improvement in cognitive tasks, reduction of anxiety, decrease in the accumulation of amyloid-beta oligomers and hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins. Diazoxide may also exerts neuroprotective effects independently of K+ channel activation by decreasing neuronal excitability and activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors or by increasing currents trough α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors. Diazoxide-treated animals show a decrease in disease severity a few days after the first clinical signs are observed, corresponding to the acute inflammatory phase of the disease. Daily oral administration of diazoxide in EAE mice during the effector phase of the disease reduces the severity of the clinical signs without any apparent adverse effect. Diazoxide decreases demyelination and axonal loss, reduces tissue damage, inhibits microglial/macrophage and astrocytic activation and preserves neuron integrity. No effects are observed on the number of B and T lymphocytes infiltrating the spinal cord[1]. |
| Cell Research | The phagocytic ability of microglia is determined by the uptake of 2-μm red fluorescent microspheres by BV-2 cells. Cells are treated with diazoxide 100 μM and activated with LPS/IFN-γ and then incubated with microspheres at a concentration of 0.01% for 30 min in the dark at 37°C and 5% CO2. Cells are rinsed twice in PBS solution, pelleted at 1,000 g for 5 min and resuspended in 300 μL PBS. Cells are kept on ice and analyzed by flow cytometry.(Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | SRG-95213, Sch-6783, Proglycem |
| Molecular Weight | 230.67 |
| Formula | C8H7ClN2O2S |
| Cas No. | 364-98-7 |
| Smiles | O=S1(=O)C=2C(NC(C)=N1)=CC=C(Cl)C2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.3767 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 60 mg/mL (260.11 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (8.67 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.