Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Betahistine (Vasomotal) is a histamine analog and H1 receptor agonist that serves as a vasodilator. It is used in MENIERE DISEASE and in vascular headaches but may exacerbate bronchial asthma and peptic ulcers. Betahistine dihydrochloride is an anti-vertigo drug. It is commonly prescribed for balance disorders or to alleviate vertigo symptoms associated with Ménière's disease.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 42.00 | |
| 200 mg | In stock | $ 51.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 46.00 |




| Description | Betahistine (Vasomotal) is a histamine analog and H1 receptor agonist that serves as a vasodilator. It is used in MENIERE DISEASE and in vascular headaches but may exacerbate bronchial asthma and peptic ulcers. Betahistine dihydrochloride is an anti-vertigo drug. It is commonly prescribed for balance disorders or to alleviate vertigo symptoms associated with Ménière's disease. |
| Synonyms | PT 9 base, Vasomotal, Serc base |
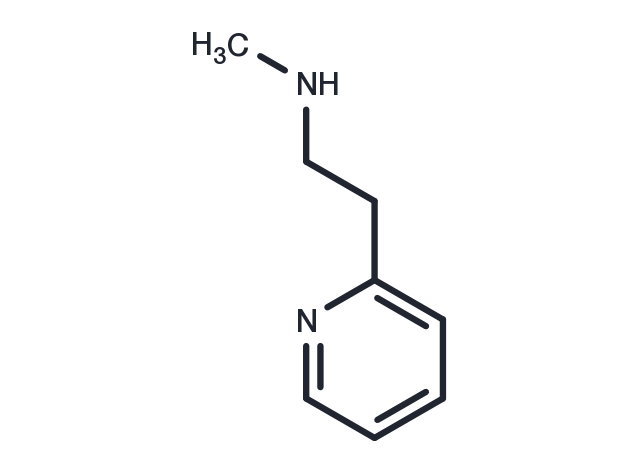
| Molecular Weight | 136.19 |
| Formula | C8H12N2 |
| CAS No. | 5638-76-6 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 30 mg/mL (220.27 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Betahistine 5638-76-6 GPCR/G Protein Immunology/Inflammation Neuroscience Histamine Receptor disease arthritis Inhibitor episode antipsychotic PT 9 base inhibit Vasomotal CIA Rheumatoid Ménière Serc base schizophrenia inhibitor
