Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


BCATc Inhibitor 2 exhibited an IC50 of 0.8 microM in the hBCATc assays; it is an active and selective inhibitor. BCATc Inhibitor 2 also blocked calcium influx into neuronal cells following inhibition of glutamate uptake, and demonstrated neuroprotective efficacy in vivo[1]. Branched-chain amino acid transferases (BCATs) have been implicated in catalyzing reversible transamination of isoleucine, leucine, and valine branched-chain amino acids to their corresponding α-keto acids, generating L-glutamate. It has been identified that there are two forms of BCAT in mammals: mitochondrial BCAT (BCATm) and cytosolic BCAT (BCATc). BCATc is expressed in particular brain region and involved in regulating glutamate synthesis for release during neuronal excitation. Thus, BCATc inhibition may be useful for the treatment of neurodegenerative and behavioral disorders involving disturbances of the glutamatergic system [2].
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | In stock | $ 51.00 | |
| 2 mg | In stock | $ 74.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 122.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 197.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 413.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 618.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 879.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 147.00 |

| Description | BCATc Inhibitor 2 exhibited an IC50 of 0.8 microM in the hBCATc assays; it is an active and selective inhibitor. BCATc Inhibitor 2 also blocked calcium influx into neuronal cells following inhibition of glutamate uptake, and demonstrated neuroprotective efficacy in vivo[1]. Branched-chain amino acid transferases (BCATs) have been implicated in catalyzing reversible transamination of isoleucine, leucine, and valine branched-chain amino acids to their corresponding α-keto acids, generating L-glutamate. It has been identified that there are two forms of BCAT in mammals: mitochondrial BCAT (BCATm) and cytosolic BCAT (BCATc). BCATc is expressed in particular brain region and involved in regulating glutamate synthesis for release during neuronal excitation. Thus, BCATc inhibition may be useful for the treatment of neurodegenerative and behavioral disorders involving disturbances of the glutamatergic system [2]. |
| Targets&IC50 | BCATm (rat):3.0 μM (IC50), BCATc (rat):0.2 μM (IC50), BCATc (human):0.8 μM (IC50) |
| In vitro | BCATc inhibition is likely to be useful for the treatment of neurodegenerative and other neurological disorders involving disturbances of the glutamatergic system. In the hBCATc assays, BCATc Inhibitor 2 exhibited an IC50 of 0.8 ± 0.05 μM. In a recombinant rat BCATc assay and a crude rat BCATm assay, the IC50 was 0.2 μM ± 0.02 and 3.0 μM ± 0.5 (n=5), respectively. BCATc Inhibitor 2 decreased calcium influx in neuronal cultures with an IC50 of 4.8 ± 1.2 μM (n=4) [1]. |
| In vivo | BCATc Inhibitor 2 blocked calcium influx into neuronal cells following inhibition of glutamate uptake, and demonstrated neuroprotective efficacy in vivo. In Lewis rats, after treatment with 30 mg/kg BCATc Inhibitor 2 (subcutaneous injection), the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) reached 8.28 μg/ml at 0.5 h (tmax). The mean plasma exposure (AUC) value was 19.9 μg h/ml, and the mean terminal half-life ranged from 12 to 15 h, indicating favorable PK parameters of BCATc Inhibitor 2. Daily administration of the mitochondrial neurotoxin, 3-nitroproprionic acid (3-NP) produced striatal lesions and led to motor deficits. Administration of BCATc Inhibitor 2 for 9 days almost completely reversed the effects of 3-NP [1]. |
| Molecular Weight | 418.77 |
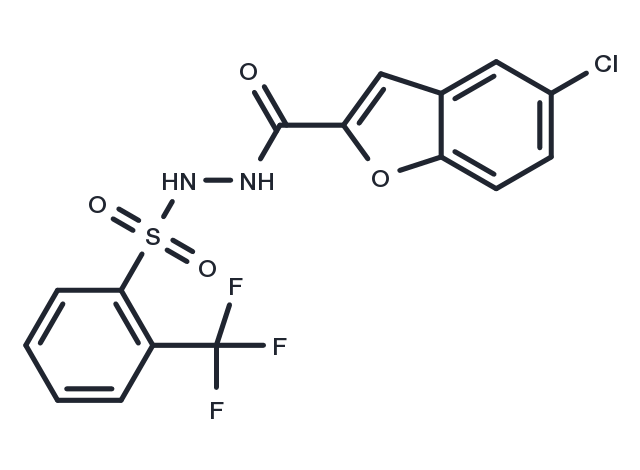
| Formula | C16H10ClF3N2O4S |
| CAS No. | 406191-34-2 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 65 mg/ml (155.22 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
BCATc Inhibitor 2 406191-34-2 Others cytosolic neurodegenerative human BCATc Inhibitor-2 mitochondrial disease rBCATc Inhibitor BCAT rBCATm inhibit hBCATc BCATc Inhibitor2 inhibitor
