Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Acetylcysteine (NAC) is an N-acetyl derivative of cysteine, a ROS inhibitor and mucolytic agent. Acetylcysteine induces apoptosis, can be used to reduce mucus thickness, and has anti-influenza viral activity.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 g | $33 | - | In Stock | |
| 10 g | $42 | - | In Stock |
| Description | Acetylcysteine (NAC) is an N-acetyl derivative of cysteine, a ROS inhibitor and mucolytic agent. Acetylcysteine induces apoptosis, can be used to reduce mucus thickness, and has anti-influenza viral activity. |
| Targets&IC50 | PC9 cells:15.53 mM, T24 cells:33.33 mM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human bladder cancer cells T24 were treated with Acetylcysteine (5-50 mM) for 24 h. Cell viability was measured by MTT. RESULTS: Acetylcysteine dose-dependently inhibited the cell viability of T24 cells with an IC50 of 33.33 mM.[1] METHODS: Rat cardiomyocytes H9c2 were treated with Acetylcysteine (2-4 mM) for 12-24 h, and apoptosis was detected by Flow Cytometry. RESULTS: Acetylcysteine dose- and time-dependently induced apoptosis in H9c2 cells. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To investigate the effects on apoptotic liver injury in mice, Acetylcysteine (150 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to CD-1 mice as a single injection, and GalN/LPS was used to induce hepatic injury 30 min later. RESULTS: Acetylcysteine pretreatment significantly attenuated GalN/LPS-induced hepatocyte apoptosis.Acetylcysteine attenuates GalN/LPS-induced apoptotic liver injury through its potent ROS scavenging and anti-apoptotic effects. [3] METHODS: To assay in vivo activity, Acetylcysteine (500 mg/kg) was administered orally to R6/1 transgenic mice with Huntington's disease (HD) once daily for nine weeks. RESULTS: Chronic Acetylcysteine administration delayed the onset and development of motor deficits in R6/1 mice and also had antidepressant-like effects in both R6/1 and wild-type mice. [4] |
| Cell Research | For survival experiments, washed cells are resuspended in RPM1 1640 medium and plated in 0.5 mL at a density of 8-10×105 per well in 24 well plastic culture dishes coated with rat tail collagen. To feed, but to avoid loss of floating cells, fresh medium (0.2 mL) is added to the cultures on days 1, 5, and 10. For experiments involving 'primed' PC12 cells, cultures are pretreated for l-2 weeks with NGF in RPM1 1640 medium supplemented with 1% heat-iN-acetylcysteinetivated horse serum. The cells are then washed and passaged into serum-free RPM1 1640 medium. |
| Animal Research | Rats are randomly allocated into five groups: sham group (n=5), control group with IIR (n=8) and three groups with IIR who are given N-acetylcysteine in different dosages: 150 mg/kg intraperitoneally 5 min before ischemia (n=8, group N-acetylcysteine 150), 300 mg/kg i.p 5 min before ischemia (n=7, group N-acetylcysteine 300), and 150 mg/kg i.p 5 min before ischemia plus 150 mg/kg 5 min before reperfusion (n=7, group N-acetylcysteine 150 + 150). After 4 h of reperfusion, the animals are euthanized by exsanguination from the abdominal aorta.[1] |
| Synonyms | N-Acetyl-L-cysteine, N-Acetylcysteine, N-Acetyl Cysteine, NAC, LNAC |
| Molecular Weight | 163.19 |
| Formula | C5H9NO3S |
| Cas No. | 616-91-1 |
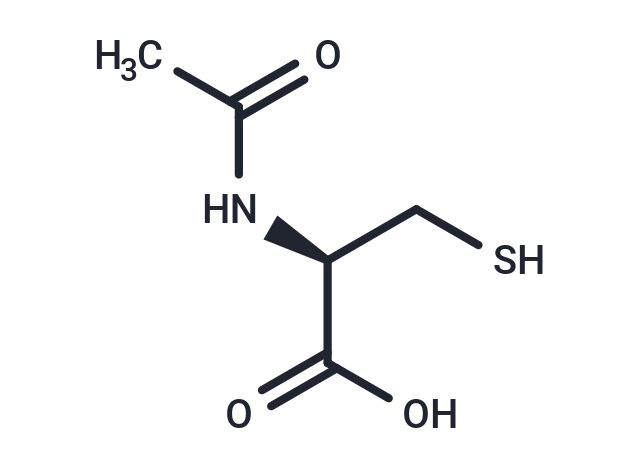
| Smiles | [C@@H](NC(C)=O)(C(O)=O)CS |
| Relative Density. | 1.249 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | keep away from moisture,The compound is unstable in solution. Please use soon | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 60 mg/mL (367.67 mM), The compound is unstable in solution, please use soon. Ethanol: 31 mg/mL (189.96 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 100 mg/mL (612.78 mM), Sonication and heating are recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: 2.5 mg/mL (15.32 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO/H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.