 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

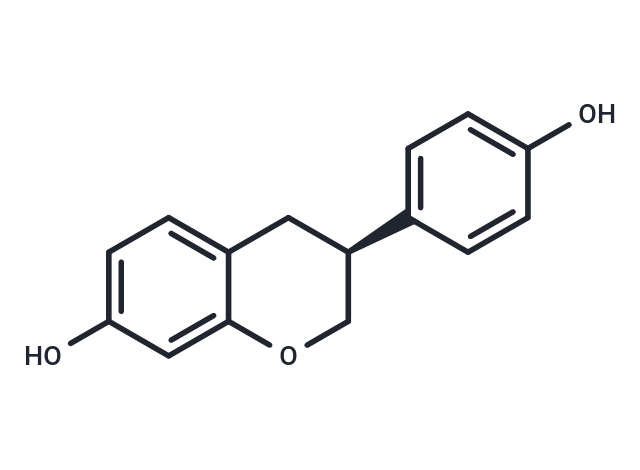
(-)-(S)-Equol (4',7-Dihydroxyisoflavan) is an orally bioavailable, non-steroidal estrogen naturally produced by the metabolism of the isoflavonoid daidzein by human intestinal microflora, with potential chemoprotective and estrogen receptor (ER) modulating activities. S-equol preferentially binds to and activates the beta isoform of ER in certain target tissues, while having an antagonistic effect in other tissues. This modulates the expression of ER-responsive genes in a tissue-specific manner. This agent may increase bone mineral density, affect vasomotor symptoms, and may decrease the proliferation rate of susceptible cancer cells. In addition, this agent interferes with the activity of enzymes involved in steroid biosynthesis. S-equol inhibits dihydrotestosterone (DHT) production and may inhibit the proliferation of androgen-driven prostate cancer. S-equol is the biologically active enantiomer while R-equol is essentially inactive and has a weak affinity for alpha-ER.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $43 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $61 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $101 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $173 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $303 | - | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $743 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $48 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | (-)-(S)-Equol (4',7-Dihydroxyisoflavan) is an orally bioavailable, non-steroidal estrogen naturally produced by the metabolism of the isoflavonoid daidzein by human intestinal microflora, with potential chemoprotective and estrogen receptor (ER) modulating activities. S-equol preferentially binds to and activates the beta isoform of ER in certain target tissues, while having an antagonistic effect in other tissues. This modulates the expression of ER-responsive genes in a tissue-specific manner. This agent may increase bone mineral density, affect vasomotor symptoms, and may decrease the proliferation rate of susceptible cancer cells. In addition, this agent interferes with the activity of enzymes involved in steroid biosynthesis. S-equol inhibits dihydrotestosterone (DHT) production and may inhibit the proliferation of androgen-driven prostate cancer. S-equol is the biologically active enantiomer while R-equol is essentially inactive and has a weak affinity for alpha-ER. |
| Targets&IC50 | ERRβ:0.73 nM(Ki) |
| In vitro | Equol is a metabolite produced from the soy phytoestrogen daidzein by the action of gut microflora. Equol has higher affinity for both ERs (estrogen receptors including ERalpha and ERbeta). Equol exists as the enantiomers R-equol and S-equol. S-equol has a high binding affinity, preferential for ERbeta with a Ki of 16 nM whereas R-equol binds more weakly and with a preference for ERalpha K with a Ki of 50 nM. [1] Equol is superior to all other isoflavones in its antioxidant activity. [2] Equol has antioestrogenic properties. [3] Equol is a 100-fold more potent than daidzein in stimulating an oestrogenic response. Equol is also more effective than daidzein in competing with 3 H-oestradiol for binding to the ER. Equol stimulates the growth of MCF-7 cells in a concentration-dependent manner. Although equol exhibits oestrogenic activity, exposure of MCF-7 cells to equol simultaneously with oestradiol is effective in reducing pS2 mRNA expression. Equol results in the downregulation of ER mRNA expression. [4] |
| Cell Research | Each well of a 24-well plate is seeded with 1 × 105 MCF-7 cells in 1 mL of media B. Twenty-four hours after plating, equol at the indicated concentration is added. Equol is dissolved in ethanol (final concentration of ethanol in the medium is 1%). The medium is changed every 24 hours and equol is replenished with each change. Cell growth is determined on the sixth day by the sulphorhodamine colorimetric assay. After colour development, aliquots are pipetted into a 96-well microtitre plate and the absorbance is determined at 570 nm using an Elisa microplate reader.(Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | Equol, 4',7-Isoflavandiol, 4',7-Dihydroxyisoflavan, (−)-Equol |
| Molecular Weight | 242.27 |
| Formula | C15H14O3 |
| Cas No. | 531-95-3 |
| Smiles | OC=1C=C2C(C[C@H](CO2)C3=CC=C(O)C=C3)=CC1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.286 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 250 mg/mL (1031.91 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 24.2 mg/mL (99.89 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (8.26 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.