 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

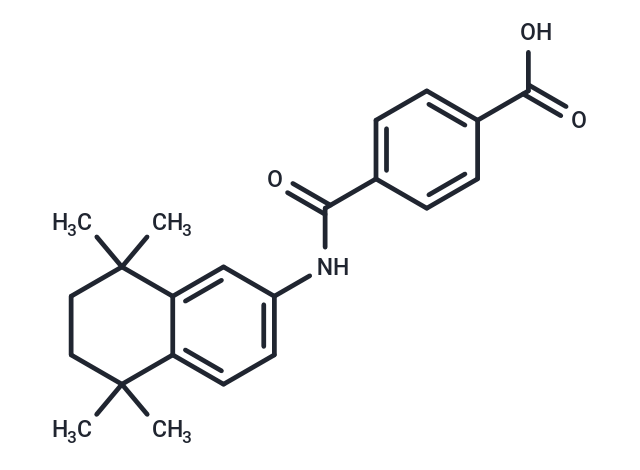
Tamibarotene (Amnolake) is an orally active, synthetic retinoid, developed to overcome all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) resistance, with potential antineoplastic activity.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | $39 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $58 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $72 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $98 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $155 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $262 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $389 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $39 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Tamibarotene (Amnolake) is an orally active, synthetic retinoid, developed to overcome all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) resistance, with potential antineoplastic activity. |
| In vitro | Tamibarotene treatment significantly reduces the levels of insoluble amyloid beta (Aβ) in the mice's brain, particularly Aβ(42), without notably affecting the levels of soluble Aβ. |
| In vivo | Tamibarotene induced HL-60 cell adhesion to endothelial cells was 38% lower compared to all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA). However, its ability to induce NB4 cell adhesion to endothelial cells was comparable to ATRA. In HL-60 cells, tamibarotene uniquely promoted early-phase induction of CD38 gene transcription through DR-RARE with intron 1 and late-phase induction through RARE lacking a 5' flanking region, resulting in lower CD38 induction than ATRA. Tamibarotene's growth inhibition on peripheral blood mononuclear cells was negligible, but it significantly inhibited growth in HTLV-I infected T-cell lines and ATL cell markers. It induced G1 phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HTLV-I infected T-cell lines, inhibited phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha and NF-κB-DNA binding, reduced expression of proteins involved in G1/S phase cell cycle transition and apoptosis, and suppressed JunD expression, inhibiting AP-1 DNA binding. Tamibarotene slightly inhibited the growth of myeloma cells and HUVECs, and significantly inhibited VEGF-stimulated HUVEC growth. While having minimal growth inhibition on bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC), tamibarotene significantly inhibited HUVEC migration when co-cultured with myeloma cells and inhibited VEGF-induced phosphorylation of the VEGF receptor. Tamibarotene markedly suppressed the formation of in vitro tubular structures and neovascularization induced by VEGF in mouse cornea. |
| Cell Research | The CellTiter Aqueous Non-Radioactive Cell Proliferation Assay Kit is used to assess cell growth. Briefly, 10,000 cells per well are seeded in a 96-well plate and cultured in RPMI containing 2% charcoal-stripped FBS and indicated retinoid concentrations for 72 hours. At the end of the treatment period, the MTS reagent is added, cells are incubated an additional 2-4 hours, and absorbance is measured at 490 nanometers. |
| Synonyms | NSC 608000, Amnolake, Am 80 |
| Molecular Weight | 351.44 |
| Formula | C22H25NO3 |
| Cas No. | 94497-51-5 |
| Smiles | CC1(C)C=2C(=CC(NC(=O)C3=CC=C(C(O)=O)C=C3)=CC2)C(C)(C)CC1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.154 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 250 mg/mL (711.36 mM), Sonication is recommended. 1.1eq. NaOH: 35.1 mg/mL (99.87 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (5.69 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1.1eq. NaOH/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.