 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Diphenhydramine hydrochloride (DPH) is a histamine H1 antagonist used as an antitussive and antiemetic. It is also used for pruritus and dermatoses, for hypersensitivity reactions, as an antiparkinson, a hypnotic, and as an ingredient in common cold preparations.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg | $29 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $44 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Diphenhydramine hydrochloride (DPH) is a histamine H1 antagonist used as an antitussive and antiemetic. It is also used for pruritus and dermatoses, for hypersensitivity reactions, as an antiparkinson, a hypnotic, and as an ingredient in common cold preparations. |
| In vitro | Diphenhydramine blocks tetrodotoxin-sensitive (TTX-S) and tetrodotoxin-resistant (TTX-R) sodium currents with K(d) values of 48 mM and 86 mM, respectively, at a holding potential of -80 mV. Diphenhydramine shifts the conductance-voltage curve for TTX-S sodium currents in the depolarizing direction but has little effect on that for TTX-R sodium currents. Diphenhydramine causes a shift of the steady-state inactivation curve for both types of sodium currents in the hyperpolarizing direction. Diphenhydramine produces a profound use-dependent block when the cells are repeatedly stimulated with high-frequency depolarizing pulses. [1] Diphenhydramine induces apoptosis in a dose- and time-dependent manner in both CCRF-CEM and Jurkat cell lines, whereas Cimetidine fails to induce significant effects at similar concentrations. Diphenhydramine-induced apoptosis is evaluated in terms of morphology, flow cytometry, and the release of cytochrome c to the cytosol. Diphenhydramine inhibits cell proliferation without inducing apoptosis in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. [2] Diphenhydramine (500 nM) significantly reduces the baseline firing of the periaqueductal gray neurons without a significant effect on the frequency of postsynaptic potentials. Diphenhydramine at high concentration inhibits periaqueductal gray neurons, but at low concentrations it has no effect on the baseline-firing rate and it blocks the response to neurotensin and tomedial preoptic nucleus stimulation. [3] |
| Synonyms | DPH, Diphenhydramine HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 291.82 |
| Formula | C17H22ClNO |
| Cas No. | 147-24-0 |
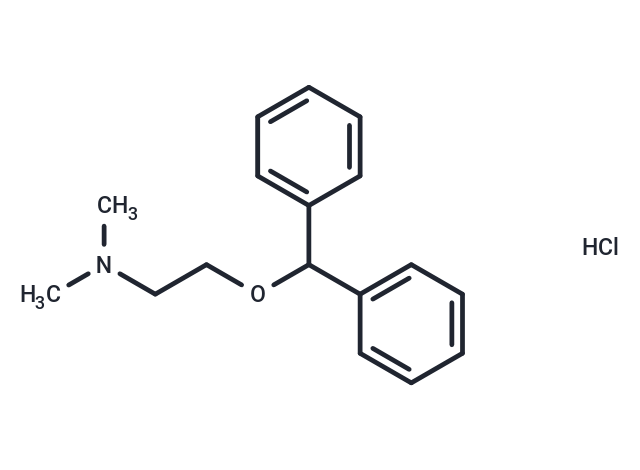
| Smiles | CN(CCOC(c1ccccc1)c1ccccc1)C.Cl |
| Relative Density. | 1.0489 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 45 mg/mL (154.2 mM), Sonication and heating are recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (6.85 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.