Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

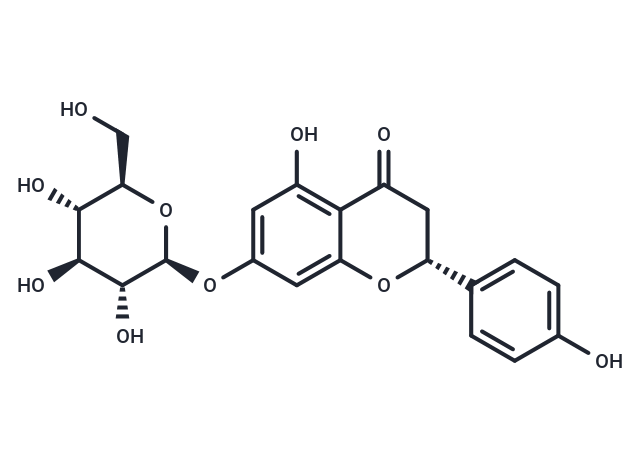
Prunin (Naringenin 7-0-glucoside) possesses anti-diabetic, and anti-abacterial properties, it can inhibit protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) and stimulate glucose uptake in insulin-resistant HepG2 cells; it also can stimulate growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and different Bacilllus sp. Prunin exhibits a markedly enhanced solubility compared to naringenin and naringin while maintaining the in vitro inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $128 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $277 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $473 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $759 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $987 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $1,380 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $1,860 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $278 | In Stock |
| Description | Prunin (Naringenin 7-0-glucoside) possesses anti-diabetic, and anti-abacterial properties, it can inhibit protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) and stimulate glucose uptake in insulin-resistant HepG2 cells; it also can stimulate growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and different Bacilllus sp. Prunin exhibits a markedly enhanced solubility compared to naringenin and naringin while maintaining the in vitro inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. |
| In vitro | The effects of Prunin- and HG-alkyl (C4-C18) esters (0.1-100μM) on human leukemia T (Jurkat) cells viability and plasma membrane fluidity were evaluated. At this concentration, cell hyperpolarization and shrinkage were also observed. Cell plasma membrane fluidity was not affected, regardless the depths of the membrane level evaluated, but mild changes in plasma membrane hydration were found. Esterification did not affect the antioxidant capacity of Prunin and HG (0.1-10μM) against 1mM H2O2. When exposed to 1mM AAPH, P-alkyl esters retained Prunin antioxidant capacity, but HG-derivatives acted as pro-oxidants[1] |
| Alias | Naringenin 7-0-glucoside |
| Molecular Weight | 434.39 |
| Formula | C21H22O10 |
| Cas No. | 529-55-5 |
| Smiles | OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](Oc2cc(O)c3C(=O)C[C@@H](Oc3c2)c2ccc(O)cc2)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O |
| Relative Density. | 1.597g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 25 mg/mL (57.55 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.