Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Oxaliplatin (L-OHP) is a DNA alkylating agent, an inhibitor of DNA synthesis. Oxaliplatin causes DNA cross-linking damage, preventing DNA replication and transcription and leading to cell death. Oxaliplatin induces autophagy.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $40 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $50 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $68 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $117 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $139 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Oxaliplatin (L-OHP) is a DNA alkylating agent, an inhibitor of DNA synthesis. Oxaliplatin causes DNA cross-linking damage, preventing DNA replication and transcription and leading to cell death. Oxaliplatin induces autophagy. |
| Targets&IC50 | U-87MG cells:17.6 μM, SK-MEL-2 cells:30.9 μM, A2780 cells:0.17 μM, HT29 cells:0.33 μg/mL, HT144 cells:7.85 μM, RT4 cells:11 μM, HT29 cells:0.97 μM, WiDr cells:0.13 μg/mL, U-373MG cells:2.95 μM, LS174T cells:0.19 μg/mL, TCCSUP cells:15 μM, SW620 cells:1.13 μg/mL |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human colon cancer cells HT29, SW620, WiDr and LS174T were treated with Oxaliplatin (0.001 ng/ml-100 µg/mL) for 24 h, and cytotoxicity was detected using MTT method.
RESULTS: Oxaliplatin was cytotoxic to HT29, SW620, WiDr and LS174T cells, with IC50s of 0.33, 1.13, 0.13 and 0.19 μg/mL, respectively.[1] METHODS: Human colon cancer cells HCT116 WT and CHK2 KO were treated with Oxaliplatin (40 µM) for 24-96 h. Apoptosis was detected by Flow Cytometry. RESULTS: Oxaliplatin treatment for 24-96 h increased apoptosis levels in WT and CHK2-KO cell lines. From 24-72 h, the apoptosis level of WT cells was consistently twofold lower than that of CHK2 KO cells. However, treatment for 96 h resulted in the same level of apoptosis in WT and CHK2-KO cells (85%). [2] METHODS: Human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells CAL27 and SCC25 were treated with Oxaliplatin (31.25-125 μM) and Oxaliplatin (25-100 μM) for 12-36 h. Cell migration was detected using the Wound-healing method. RESULTS: Oxaliplatin inhibited the migration of CAL27 and SCC25 cells in a dose-dependent manner. [3] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To detect anti-tumor activity in vivo, Oxaliplatin (5 mg/kg) and piperlongumine (2.5 mg/kg) were administered intraperitoneally once a day for twenty-four days to BALB/c nu/nu mice bearing human colorectal carcinoma tumor HCT-116.
RESULTS: The combination of Oxaliplatin and piperlongumine significantly inhibited tumor growth, and piperlongumine sensitized tumors to Oxaliplatin through ROS-mediated apoptosis in vivo. [4] METHODS: To model platinum-induced painful peripheral neuropathy, Oxaliplatin (3 mg/kg/day) was injected intraperitoneally into C57BL6J mice for five days with five days of rest for two cycles. RESULTS: Mice in the Oxaliplatin-treated group exhibited significant mechanical anomalous pain. the Oxaliplatin group exhibited significant cold nociceptive hypersensitivity in the hindfoot. [5] |
| Kinase Assay | Binding experiments of electrophysiology: CHO cells expressing the subunit of the voltage-dependent L-type Ca2+ channel are cultrured in medium without serum in the presence of different concentrations of Nisoldipine. Then Ca2+ channel current elicited from a holding potential of -100 mV or -50 mV is recorded at room temperature with the whole-cell configuration of the patch-clamp method using the List EPC-7 patch-clamp amplifer and pClamp software. The concentration of competitor inhibiting 50% of the specific binding represents IC50. |
| Cell Research | The cytotoxicity studies are carried out with the sulforhodamine-B microculture colorimetrie assay. Typically, cells are plated into 96-well plates on day 0 and exposed to Oxaliplatin on day 1; the sulforhodamine-B assay is carried out 48 h after Oxaliplatin exposure. The plates are incubated at 37 °C in 5% CO2 and 100% relative humidity at all times except when adding Oxaliplatin and during the final assay period. The initial number of cells plated for the assay ranged from 2-20 × 103 cells/50 /nL/well. The numbers of cells for plating and the drug exposure time are based on pilot studies using the criteria that (a) the cells in control wells are still in the log phase of growth on the day of the assay; (b) the maximum absorbance for the untreated controls on the day of the assay is in the range of 1.0 to 1.5; and (c) cells go through >2 doublings during the drug exposure. Eight wells are used per concentration. The plates are read at 570 and/or 540 nm using a Biotek Instruments model EL309 microplate reader interfaced with an IBM PC-compatible computer. The data are transferred and transformed into a LOTUS 1-2-3 format by the computer program DATALOG, and survival fractions are calculated by comparing the drug treated with control(Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | L-OHP |
| Molecular Weight | 397.29 |
| Formula | C8H14N2O4Pt |
| Cas No. | 61825-94-3 |
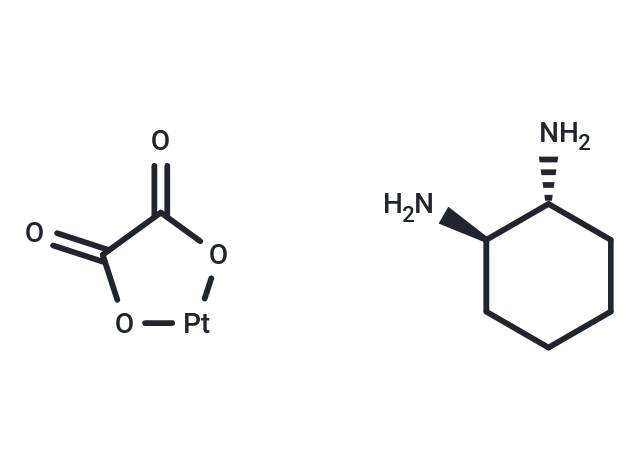
| Smiles | O=C1O[Pt]OC1=O.N[C@@H]1CCCC[C@H]1N |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble) DMSO: 50 mg/mL (125.85 mM), DMSO inactivates the activity of Oxaliplatin. H2O: 2.5 mg/mL (6.29 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMF: 1.67 mg/mL (4.2 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMF/H2O/DMSO
H2O/DMSO
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.