Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
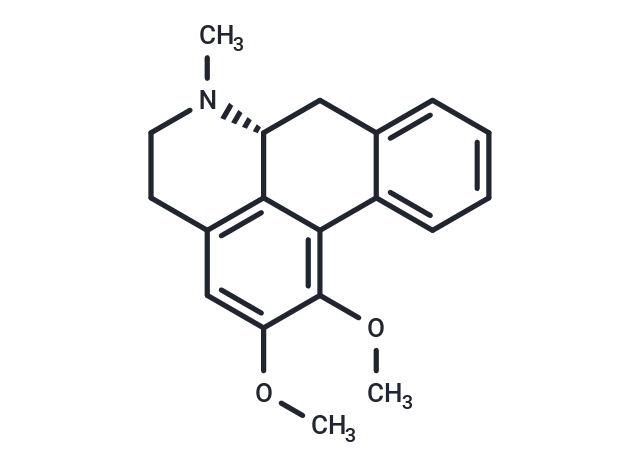
Nuciferine ((-)-Nuciferine) is an alkaloid found within the plants Nymphaea caerulea and Nelumbo nucifera. It has a profile of action associated with dopamine receptor blockade.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $39 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $55 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $122 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $178 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $268 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $655 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $43 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Nuciferine ((-)-Nuciferine) is an alkaloid found within the plants Nymphaea caerulea and Nelumbo nucifera. It has a profile of action associated with dopamine receptor blockade. |
| Targets&IC50 | D4:2 μM (EC50), 5-HT2C:131 nM, 5-HT2B:1 μM, 5-HT1A:3.2 μM (EC50), D5:2.6 μM (EC50), 5-HT6:700 nM(EC50), 5-HT7:150 nM, D2:64 nM (EC50), 5-HT2A:478 nM |
| In vitro | Nuciferine is a partial agonist at DD2 receptor with an activity (Emax=67% of dopamine) similar to aripiprazole (Emax=50% of dopamine). In line with its partial agonist activity, Nuciferine inhibited dopamine-induced activation of Gi with a potency similar to clozapine (Nuciferine KB=62 nM; Clozapine KB=20 nM) as determined via Schild regression analysis[1]. The natural product Nuciferine acts as an effective inhibitor of adult worm motility. Nuciferine is effective at inhibiting both basal and 5-HT evoked motility of adult schistosomes. Nuciferine inhibits Sm.5HTRL and schistosomule with 0.24±0.04 and 0.62±0.22 μM, respectively[2]. |
| In vivo | In studies using rodent models to evaluate the effects of antipsychotic drugs, Nuciferine demonstrated several significant actions: it inhibited the head-twitch responses and the discriminative stimulus effects caused by a 5-HT2A agonist, effectively replaced the discriminative stimulus of clozapine, increased locomotor activity induced by amphetamine, and reduced both the locomotor activity prompted by phencyclidine (PCP) and the disruption of prepulse inhibition caused by PCP, all without causing catalepsy. When administered with cumulative doses of PCP, Nuciferine at concentrations of 1 or 3 mg/kg did not alter the PCP's effects. However, when given to animals trained to recognize clozapine, Nuciferine at a dose of 10 mg/kg induced a response comparable to clozapine (with 80.63% of the responses corresponding to the drug lever) and had an effective dose (ED50) of 5.42 mg/kg (with a 95% confidence interval between 3.09 and 9.48 mg/kg), unlike lower doses (0.1 mg/kg-3 mg/kg), which did not mimic clozapine's discriminative cue. Moreover, at 10 mg/kg, Nuciferine significantly reduced the activity rate compared to the control group treated with a vehicle, indicating a substantial therapeutic effect (p<0.001). |
| Kinase Assay | For affinity determination, Nuciferine is subjected to primary radioligand binding assays tested at a single 10 μM concentration to displace 50% of the radioligand at a given receptor target. If a more than 50% of the radioligand is displaced, Nuciferine is selected for a secondary binding assay tested at 11 concentrations in triplicate in competition with the radioligand to generate an IC50 and Ki. Binding assays are performed in 96-well plates with 125 μL per well in appropriate binding buffer using radioligand at or near the Kd. Plates are incubated at room temperature in the dark for 90 min. Reactions are stopped by vacuum filtrations onto 0.3% polyethyleneimine soaked 96-well filter mats using a 96-well Filtermate harvester, followed by at least three washes of cold wash buffer. Scintillation cocktail is melted onto dried filters and radioactivity is counted using a Wallac Trilux Microbeta[1]. |
| Cell Research | Nuciferine is dissolved in DMSO and stored, and then diluted with appropriate medium before use[1]. Cells are plated into 48-well plates one day before uptake is performed. Cells are washed with 0.5 mL uptake buffer (4 mM Tris, 6.25 mM HEPES, 120 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 1.2 mM CaCl2, 1.2 mM MgSO4, 5.6 mM D-glucose, 1.7 mM ascorbic acid, and 1 μM pargyline, pH 7.4). Cells are incubated with 225 μL uptake buffer with or without the indicated concentration of Nuciferine for 15 minutes. After incubation, 25 μL uptake buffer containing 3H-DA and DA is added for a final concentration of 20 nM 3H-DA and 1 μM DA. Cells are incubated at 37°C for 20 minutes or for the time indicated. Nonspecific uptake is determined in the presence of 10 μM nomifensine. Uptake is terminated by aspirating uptake buffer and washing each well twice with 0.5 mL ice-cold uptake buffer. Cells are lysed in 0.1 N NaOH and transferred to vials containing 3 mL scintillation cocktail. Radioactivity is quantitated using a Beckman LS6500 counter. Data are analyzed in Graph Pad Prism 5.0[1]. |
| Synonyms | VLT 049, Sanjoinine E, (-)-Nuciferine |
| Molecular Weight | 295.38 |
| Formula | C19H21NO2 |
| Cas No. | 475-83-2 |
| Smiles | COc1cc2CCN(C)[C@@H]3Cc4ccccc4-c(c1OC)c23 |
| Relative Density. | 1.15g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 2.96 mg/mL (10.02 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 1 mg/mL (3.39 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.