Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
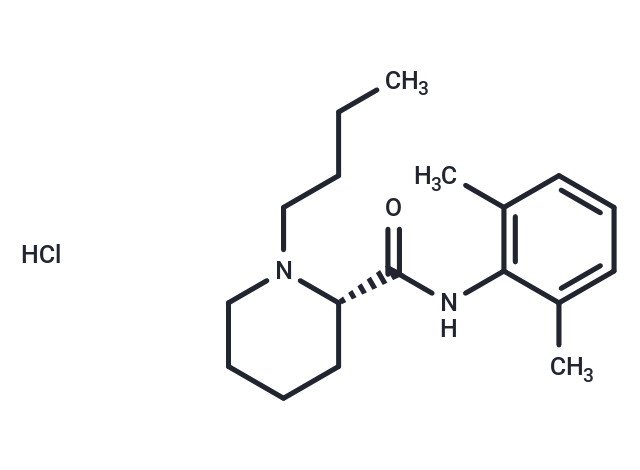
Levobupivacaine hydrochloride ((S)-(-)-Bupivacaine monohydrochloride) is a reversible neuronal sodium channel inhibitor and the pure S(-)-enantiomer of bupivacaine, used as a long-acting local anesthetic.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $32 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $40 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $52 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $112 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $166 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Levobupivacaine hydrochloride ((S)-(-)-Bupivacaine monohydrochloride) is a reversible neuronal sodium channel inhibitor and the pure S(-)-enantiomer of bupivacaine, used as a long-acting local anesthetic. |
| In vitro | Levobupivacaine is an amide-type local anaesthetic. Levobupivacaine acts via blockade of voltage-sensitive ion channels in neuronal membranes, preventing transmission of nerve impulses. Localised and reversible anaesthesia is produced by interference with the opening of the sodium channel, which inhibits conduction of the action potential in nerves involved in sensory and motor activity and sympathetic activity. [1] Levobupivacaine displaces 3H-BTX from sodium channels of rat brain synaptosomes with IC50 of 2.9 μM and Hill coefficients of 1.2. When cell membrane is held at -80 mV, -70 mV, -60 mV or -100 mV, Levobupivacaine shows tonic inhibition of sodium channel in GH3 cells with IC50s of 132.1, 37.6, 21.6 and 264 μM, respectively. [2] Levobupivacaine depresses action potential of isolated axon in vitro. Levobupivacaine (1 mM) depresses action potential amplitude and maximal rate of rise of action potential (dV/dtmax) in the crayfish giant axons with value of 88 and 81 respectively, after perfusion for 15 min. [3] Levobupivacaine also displays activity on cardiac ion channels. In isolated ventricular myocytes, the apparent affinity for inactivated state of the sodium channel is 4.8 μM for Levobupivacaine, with a calculated KD of 39 μM. On inhibition of cardiac delayed rectifier potassium channels (hKv1.5), the steady-state block for Levobupivacaine (20 μM) is 31%, with a calculated KD of 27.3 μM. Levobupivacaine may also inhibit cardiac calcium channels. 10 μM Levobupivacaine produces a 50% decrease in contractile force of guinea-pig papillary muscles. [4] |
| In vivo | Levobupivacaine has similar nerve blocking potency with bupivacaine. Levobupivacaine at a dose of 0.125%, inhibits motor and nocifensive pinch responses with maximum %MPE of 99 and 68 respectively, and inhibits the duration of deficits of motor and nocifensive pinch responses (60 and 30 , respectively) after sciatic nerve block. [4] |
| Kinase Assay | Hsp90 Binding Assay: Human Hsp90α solution (0.5 μg/mL) is fixed on 96-well plates, followed by blocking with TBS containing 1% bovine serum albumin. KW-2478 solutions is added to the wells, and bRD is added to a concentration of 0.1 μmol/L. After removal of solution, poly-HRP streptavidin solution dilutes with poly-HRP dilution buffer is added to the wells. After removal of solution, equal volumes of TMB peroxidase substrate and peroxidase solution B are added to the wells. To stop the HRP reaction, 2 mol/L H2SO4 are added, followed by measurement of absorbance at 450 nm using a microplate spectrophotometer. |
| Synonyms | Levobupivacaine HCl, (S)-(-)-Bupivacaine monohydrochloride, (S)-(-)-Bupivacaine HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 324.89 |
| Formula | C18H28N2O·HCl |
| Cas No. | 27262-48-2 |
| Smiles | Cl.CCCCN1CCCC[C@H]1C(=O)Nc1c(C)cccc1C |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 53 mg/mL (163.13 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 59 mg/mL (181.6 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 50 mg/mL (153.9 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2.5 mg/mL (7.69 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/Ethanol/H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.