Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
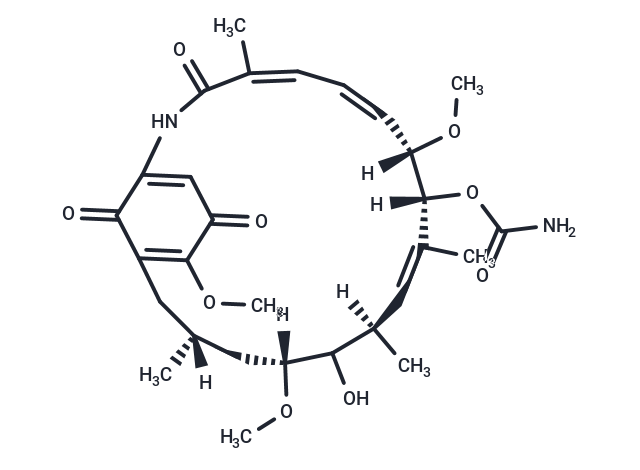
Geldanamycin, an HSP90 inhibitor (Kd: 1.2 μM), specifically disrupts glucocorticoid receptor (GR)/HSP association.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | $39 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $72 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $122 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $198 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $43 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Geldanamycin, an HSP90 inhibitor (Kd: 1.2 μM), specifically disrupts glucocorticoid receptor (GR)/HSP association. |
| Targets&IC50 | HSP90 (N-terminal domain):0.78 μM(Kd), HSP90:1.2 μM(Kd), p185:70 nM |
| In vitro | Geldanamycin binds in the ATP-binding site in the N-terminus domain of Hsp90s (residues 1-220). Geldanamycin inhibits the ATPase activity of Hsp90 in a dose-dependent manner. [1] Geldanamycin causes a dose-dependent G2 arrest and reversible inhibiton o f entry into the S phase in A2780 human ovarian cell line. This inhibition is accompanied by p53 increase and finally demonstrated to be p53 dependent. [2] Geldanamycin causes polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of the p185 receptor protein-tyrosin kinase and shows a IC50 with 70 nM. [3, 4] Geldanamycin is a typical anti-tumor reagent, shows a mean GI50 with 0.18 μM against the panel of 60 human tumor cell lines. [5] |
| In vivo | Geldanamycin (50 mg//kg) shows 30% inhibition on pl85-associated phosphotyrosine levels in FRE/erbB-2 mice. [6] |
| Kinase Assay | Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC) of Nucelotide Binding: The titration experiments are performed using the MSC system. In each experiment, 16 aliquots of 15 μL of geldanamycin (300 μM in 1% DMSO) are injected into 1.3 mL of protein (31 μM in 20 mMTris-HCl, pH 7.5, 1 mMEDTA) at 25 °C, and the resulting data are fit after subtracting the heats of dilution. Heats of dilution are determined in separate experiments from addition of geldanamycin into buffer and buffer into protein. No evidence for binding of DMSO in the nucleotide binding site is observed. Titration data are fit using a nonlinear least-squares curve-fitting algorithm with three floating variables: stoichiometry, binding constant (Kb) 1/Kd), and change of enthalpy of interaction (ΔH°). Dissociation constants estimated for geldanamycin binding to intact yeast Hsp90 is 1.22 μM, and for binding to Hsp90 N-terminal domain is 0.78 μM. No meaningful heat is observed with binding to the C-terminal fragment. |
| Cell Research | Exponentially growing cells are treated with Geldanamycin and at various times DNA synthesis is assessed by incorporation of bromodeoxyuridine (BrdUrd) and flow cytometric analysis. No marked difference in total cell number is noted during this time course for treated and untreated cultures. BrdUrd (10 μM) is incorporated over a 4-h incubation period at 37 °C and cells are harvested and fixed in 70% ethanol. After denaturation of the DNA with 2 N HC1, cells are incubated with an anti-BrdUrd mouse monoclonal antibody followed by a fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-linked goat anti-mouse IgG. Cells are stained for 30 minutes at room temperature with propidium iodide and analysed by flow cytometry using a Coulter EPICS Profile Analyzer. (Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | NSC 122750 |
| Molecular Weight | 560.64 |
| Formula | C29H40N2O9 |
| Cas No. | 30562-34-6 |
| Smiles | [H][C@@]1(C)CC2=C(OC)C(=O)C=C(NC(=O)\C(C)=C/C=C\[C@]([H])(OC)[C@]([H])(OC(N)=O)\C(C)=C/[C@@]([H])(C)C(O)[C@@]([H])(C1)OC)C2=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.2443 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Color | Yellow |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,keep away from moisture | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 49 mg/mL (87.4 mM), Heating is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.