Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


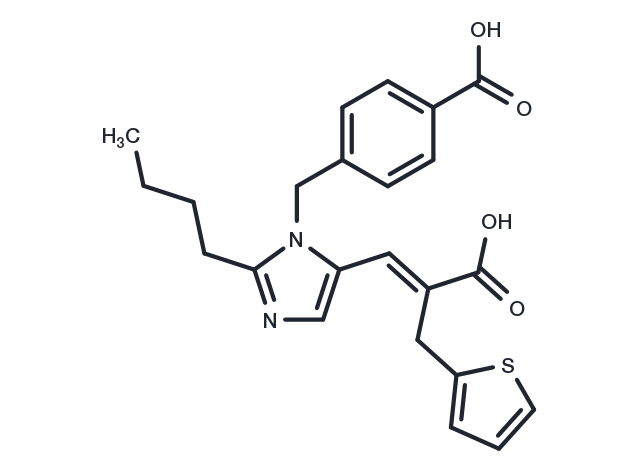
Eprosartan (SKF-108566J free base) is a selective and competitive nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist with high affinity for AT1 receptor subtypes and can be used as an antihypertensive agent.Eprosartan has an inhibitory effect on angiotensin II receptor, with IC50 values of 9.2 nM and 3.9 nM in rat and human adrenocortical membranes, respectively. The IC50 values of Eprosartan in rat and human adrenocortical membranes were 9.2 nM and 3.9 nM, respectively.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 39.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 64.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 105.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 153.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 229.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 70.00 |

| Description | Eprosartan (SKF-108566J free base) is a selective and competitive nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist with high affinity for AT1 receptor subtypes and can be used as an antihypertensive agent.Eprosartan has an inhibitory effect on angiotensin II receptor, with IC50 values of 9.2 nM and 3.9 nM in rat and human adrenocortical membranes, respectively. The IC50 values of Eprosartan in rat and human adrenocortical membranes were 9.2 nM and 3.9 nM, respectively. |
| Targets&IC50 | Mesenteric artery membranes (rat):1.5 nM, [125I] bnding to human liver membranes:1.7 nM |
| In vitro | Eprosartan (SKF-108566J) inhibits [125I]AII binding to human liver membranes with an IC50 of 1.7 nM and to rat mesenteric artery membranes with an IC50 of 1.5 nM. In rabbit aortic smooth muscle cells, Eprosartan causes a concentration-dependent inhibition of AII-induced increases in intracellular Ca2+ levels[1] |
| In vivo | In conscious normotensive rats, intravenous administration of Eprosartan (0.01-0.3 mg/kg) produced dose-dependent parallel shifts in the AII pressor dose-response curve. Intragastric or intraduodenal administration of Eprosartan (3-10 mg/kg) to conscious normotensive rats resulted in a dose-dependent inhibition of the pressor response to AII (250 ng/kg, i.v.). Significant inhibition of the pressor response to AII was observed for 3 hours at a dose of 10 mg/kg, intraduodenally[1]. |
| Synonyms | KF-108566J free base, Teveten |
| Molecular Weight | 424.51 |
| Formula | C23H24N2O4S |
| CAS No. | 133040-01-4 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: Soluble
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Eprosartan 133040-01-4 Endocrinology/Hormones RAAS KF-108566J KF-108566J free base Teveten inhibitor inhibit
