Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


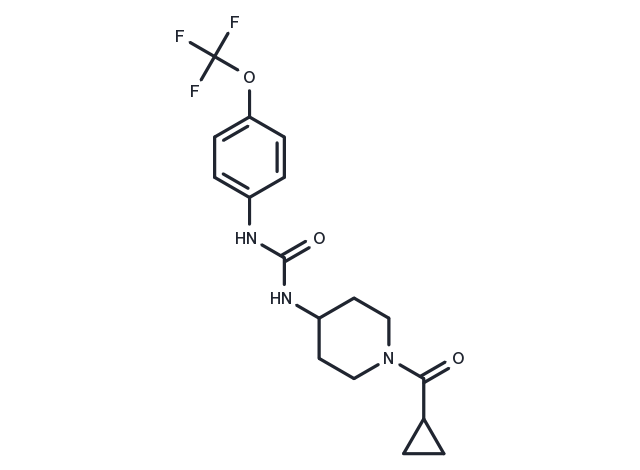
CAY10640 (sEH inhibitor-1) is a potent, orally active, water-soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitor that inhibits sEH in humans and mice with IC50s of 0.4 and 5.3 nM, respectively.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | In stock | $ 178.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 445.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 656.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 987.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 1,400.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 1,880.00 | |
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 3,780.00 |


| Description | CAY10640 (sEH inhibitor-1) is a potent, orally active, water-soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitor that inhibits sEH in humans and mice with IC50s of 0.4 and 5.3 nM, respectively. |
| Targets&IC50 | sEH (mouse):0.4 nM |
| In vivo | Oral administration of 13 1-aryl-3-(1-acylpiperidin-4-yl)urea (CAY10640) inhibitors in mice revealed substantial improvements in pharmacokinetic parameters over previously reported 1-adamantylurea based inhibitors. This novel sEH inhibitor showed a 1000-fold increase in potency when compared to morphine by reducing hyperalgesia as measured by mechanical withdrawal threshold using the in vivo carrageenan induced inflammatory pain model.[1] |
| Synonyms | sEH inhibitor-1 |
| Molecular Weight | 371.35 |
| Formula | C17H20F3N3O3 |
| CAS No. | 1208549-68-1 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMF: 4.5 mg/mL (12.2 mM)
Ethanol: 2 mg/mL
DMSO: 4.5 mg/mL (12.2 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
CAY10640 1208549-68-1 Metabolism Epoxide Hydrolase CAY 10640 sEH inhibitor-1 CAY-10640 inhibitor inhibit
