- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
2,6-Diaminoheptanedioic acid
Diaminopimelic acid or DAPA is a lysine-like amino acid derivative that is a key component of the bacterial cell wall. DAPA is incorporated or integrated into peptidoglycan of gram negative bacteria and is the attachment point for Braun's lipoprotein (BLP or Murein Lipoprotein). BLP is found in gram-negative cell walls and is one of the most abundant membrane proteins. BLP is bound at its C-terminal end (a lysine) by a covalent bond to the peptidoglycan layer (specifically to diaminopimelic acid molecules) and is embedded in the outer membrane by its hydrophobic head (a cysteine with lipids attached). BLP tightly links the two layers and provides structural integrity to the bacterial outer membrane. Diaminopimelic acid can be found in human urine or feces due to the lysis or enzymatic breakdown of gram negative gut microbes.
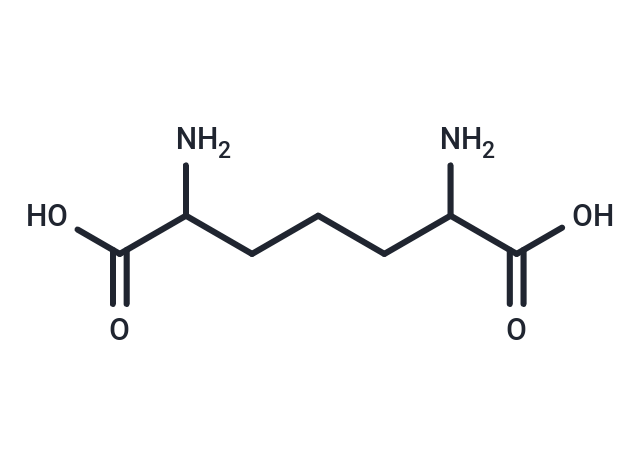
2,6-Diaminoheptanedioic acid
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $33 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $56 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $85 | In Stock |
Product Introduction
| Description | Diaminopimelic acid or DAPA is a lysine-like amino acid derivative that is a key component of the bacterial cell wall. DAPA is incorporated or integrated into peptidoglycan of gram negative bacteria and is the attachment point for Braun's lipoprotein (BLP or Murein Lipoprotein). BLP is found in gram-negative cell walls and is one of the most abundant membrane proteins. BLP is bound at its C-terminal end (a lysine) by a covalent bond to the peptidoglycan layer (specifically to diaminopimelic acid molecules) and is embedded in the outer membrane by its hydrophobic head (a cysteine with lipids attached). BLP tightly links the two layers and provides structural integrity to the bacterial outer membrane. Diaminopimelic acid can be found in human urine or feces due to the lysis or enzymatic breakdown of gram negative gut microbes. |
| Molecular Weight | 190.2 |
| Formula | C7H14N2O4 |
| Cas No. | 583-93-7 |
| Smiles | NC(CCCC(N)C(O)=O)C(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.344 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 10 mM, Sonication is recommended. DMSO: Insoluble | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Sci Citations
Calculator
In Vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Dose Conversion
Tech Support
Keywords

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.



