 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Salinomycin (Procoxacin), a polyether potassium ionophore antibiotic, specifically inhibits the growth of gram-positive bacteria, acts as a potent inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by blocking Wnt-induced LRP6 phosphorylation, and demonstrates selective activity against human cancer stem cells.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $32 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $45 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $74 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $118 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $219 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $389 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $558 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Salinomycin (Procoxacin), a polyether potassium ionophore antibiotic, specifically inhibits the growth of gram-positive bacteria, acts as a potent inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by blocking Wnt-induced LRP6 phosphorylation, and demonstrates selective activity against human cancer stem cells. |
| In vitro | Salinomycin, a potent Wnt signaling cascade inhibitor and antibiotic potassium ionophore, demonstrates significant anticancer properties. It induces apoptosis in malignant lymphocytes within 48 hours, showing a mean IC50 value of 230 nM. Notably, Salinomycin has been identified as a selective inhibitor of breast cancer stem cells (CSCs)[1], effectively inhibiting both normal and Cisp-resistant SW620 cancer cells with IC50 values of 1.54±0.23 μM and 0.32±0.05 μM, respectively. It uniquely targets and kills CSCs and therapy-resistant cancer cells. Continuous treatment with Salinomycin over 48 hours increases the apoptotic cell count significantly in Cisp-resistant SW620 cells compared to non-resistant SW620 cells, as observed under a microscope and confirmed through flow cytometric analysis of cell apoptosis. The apoptotic rate is markedly higher in Cisp-resistant SW620 cells (37.82±3.63%) than in standard SW620 cells (16.78±2.56%) (p<0.05)[2]. |
| In vivo | Upon administering doses of 4 mg/kg and 8 mg/kg Salinomycin (Sal), alongside 10 uL/g saline water to mice for a duration of 6 weeks, followed by their sacrifice, a significant reduction in liver tumor size is observed in the Sal-treated groups compared to the controls. Tumor diameters decrease notably from 12.17 mm to 3.67 mm (p<0.05), and volumes, calculated as V=length×width^2×0.5, diminish from 819 mm^3 to 25.25 mm^3 (p<0.05). Subsequent analyses, involving HE staining, immunohistochemistry, and TUNEL assays, are conducted to evaluate Salinomycin's anti-tumor efficacy. Results show altered liver cancer tissue structure, reduced PCNA expression, and higher apoptosis rates in Sal-treated mice, indicating significant anti-tumor activity. Furthermore, an increase in the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and a decrease in β-catenin protein expression corroborate Salinomycin's effectiveness. Salinomycin, a monocarboxylic acid polyether antibiotic derived from Streptomyces albus fermentation, exhibits a unique cyclic structure enabling it to bind with pathogenic microorganisms and extracellular cations of coccidia, particularly K+, Na+, Rb+, effectively altering intra- and extracellular ion concentrations[4][5]. |
| Synonyms | Procoxacin |
| Molecular Weight | 751 |
| Formula | C42H70O11 |
| Cas No. | 53003-10-4 |
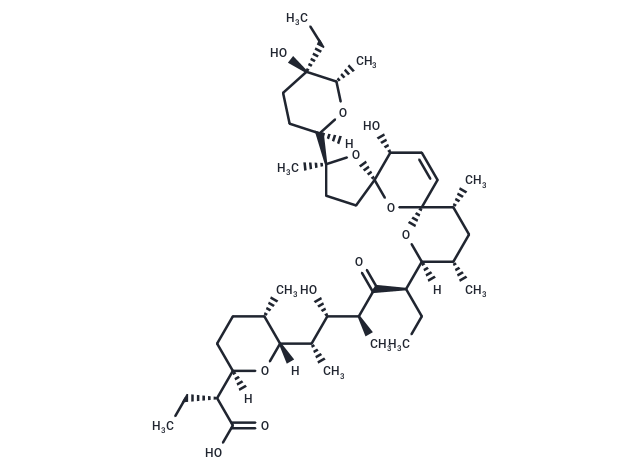
| Smiles | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@H](C)[C@@]([H])(O1)[C@@H](C)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)C(=O)[C@H](CC)[C@@]1([H])O[C@@]2(O[C@@]3(CC[C@](C)(O3)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@](O)(CC)[C@H](C)O3)[C@H](O)C=C2)[C@H](C)C[C@@H]1C)[C@@H](CC)C(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.18 g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from moisture | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 140 mg/mL (186.42 mM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.