 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Diproteverine HCl is a novel calcium antagonist with antianginal properties, antispasmodic and vasoactive.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $82 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $181 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $267 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $413 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $592 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $819 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $1,090 | - | In Stock |
| Description | Diproteverine HCl is a novel calcium antagonist with antianginal properties, antispasmodic and vasoactive. |
| In vitro | Diproteverine (1 μM; sheep Purkinje fibers) to reduce the amplitude of the slow action potential (IC30 = 2 μM) and to shorten the duration of the fast action potential at 50% repolarisation (IC30 = 2.5 μM). Papaverine was found to possess marginal membrane channel-blocking activity and to be much more potent than diproteverine as a cAMP-phosphodiesterase inhibitor (IC50 = 8 μM).[2] |
| In vivo | Diproteverine (0.25-0.75 mg/kg; i.e.; dog; at plasma levels within the assumed therapeutic range) dose-relatedly decreases heart rate, increases corrected sinus node recovery time, and decreases Wenckebach point. These effects are observed at plasma levels ranging between 16.2 +/- 4.1 and 144.7 +/- 12.5 ng/ml. After cholinergic blockade with N-methylscopolammonium, diproteverine lowers heart rate (greater than or equal to 0.25 mg/kg), increases corrected sinus node recovery time, and decreases Wenckebach point (greater than or equal to 0.5 mg/kg). After propranolol, diproteverine only significantly reduces corrected sinus node recovery time 5 min after the third administration (0.75 mg/kg). After pharmacologic autonomic blockade by N-methylscopolammonium propranolol combination, diproteverine lowers the intrinsic heart rate (greater than or equal to 0.25 mg/kg) and Wenckebach point (greater than or equal to 0.5 mg/kg). Diproteverine does not modify mean blood pressure. These results show that diproteverine administered with and without pharmacologic autonomic blockade in the conscious dog causes dose-related depressant effects on sinus node function and atrioventricular conduction without producing significant vasodilatation.[1] |
| Molecular Weight | 462.02 |
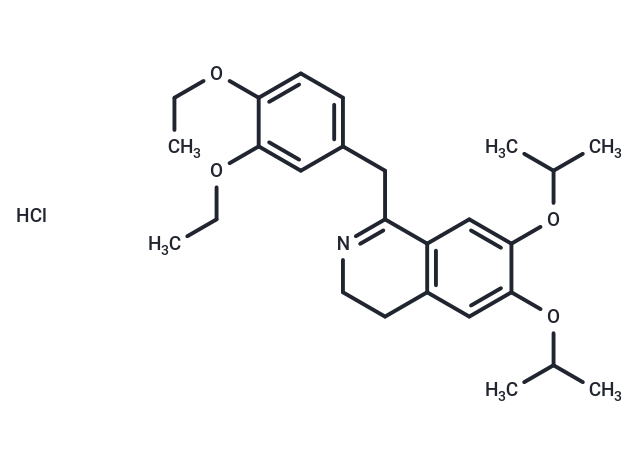
| Formula | C26H36ClNO4 |
| Cas No. | 69373-88-2 |
| Smiles | Cl.N1=C(C=2C=C(OC(C)C)C(OC(C)C)=CC2CC1)CC3=CC=C(OCC)C(OCC)=C3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 55 mg/mL (119.04 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.