Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

SAG hydrochloride (912545-86-9(free base)) (Smoothened Agonist HCl) acts as an SMO agonist.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $47 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $97 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $155 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $289 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $396 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $593 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $113 | In Stock |
| Description | SAG hydrochloride (912545-86-9(free base)) (Smoothened Agonist HCl) acts as an SMO agonist. |
| In vitro | SAG regulates Smo activity by binding directly to the Smo heptahelical bundle. [1] SAG induces Smo-dependent signaling through Gli in a GRK2-dependent way. [2] SAG also (1 nM) induces proliferation of neuronal and glial precursors without affecting the differentiation pattern of newly produced cells. |
| In vivo | In the adult rat hippocampus, the intracerebroventricular administration of SAG (2.5 nM) significantly increases the number of newly generated cells and extends survival of hippocampal cells. [3] In mice, SAG (20 μg/g, i.p.) effectively prevents GC-induced neonatal cerebellar developmental abnormalities. |
| Animal Research | Animal Models: RatFormulation: DMSODosages: 2.5 nMAdministration: Intracerebroventricular administration(Only for Reference) |
| Alias | Smoothened Agonist HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 526.52 |
| Formula | C28H29Cl2N3OS |
| Cas No. | 2095432-58-7 |
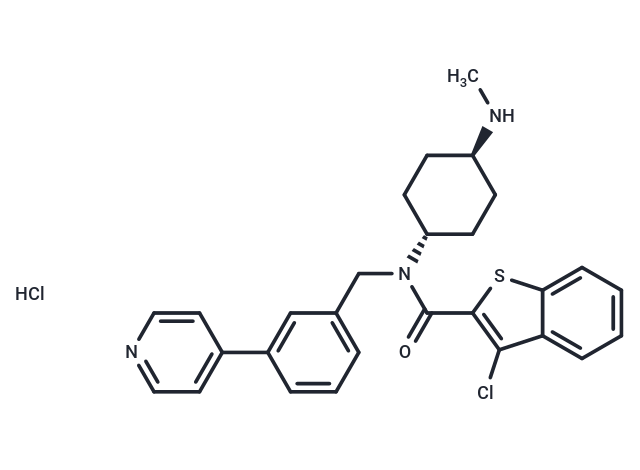
| Smiles | Cl.CN[C@H]1CC[C@@H](CC1)N(Cc1cccc(c1)-c1ccncc1)C(=O)c1sc2ccccc2c1Cl |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 38 mg/mL (72.17 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 66 mg/mL (125.35 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.