Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


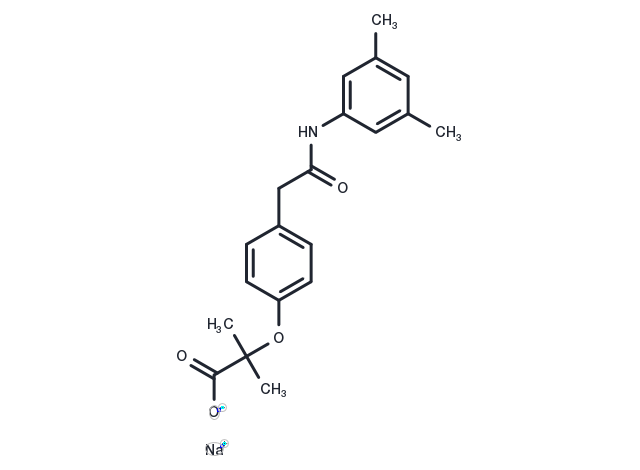
Efaproxiral Sodium (RSR13 sodium), a synthetic allosteric modifier of hemoglobin, is utilized for brain metastases originating from breast cancer.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 30.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 46.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 67.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 98.00 | |
| 200 mg | In stock | $ 143.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 68.00 |


| Description | Efaproxiral Sodium (RSR13 sodium), a synthetic allosteric modifier of hemoglobin, is utilized for brain metastases originating from breast cancer. |
| In vitro | Efaproxiral, a synthetic allosteric modifier of hemoglobinoxygen binding affinity, has been shown to bind reversibly to hemoglobin, stabilizing the deoxyhemoglobin tetramer conformation to reduce its affinity for oxygen. [1] |
| In vivo | Efaproxiral plus oxygen breathing reduces the radiobiological hypoxic fraction of EMT6 tumors from the value of 24% found in both air-breathing and oxygen-breathing mice to 9% and improves the response of the tumors to radiation. Carboplatin (100 mg/kg) slowes tumor growth in air-breathing mice, producing a growth delay of 3.3 days. Efaproxiral plus oxygen increases the growth delay to 5.7 days; this is 2.4 days (71%) greater than that for carboplatin alone and 2.1 days (57%) greater than that for carboplatin plus oxygen breathing. Efaproxiral plus oxygen breathing, therefore, improves the tumor growth delay obtained with 100 mg/kg carboplatin to or beyond that obtained with the highly toxic dose of 150 mg/kg carboplatin, but does so without increasing the toxicity beyond that seen with 100 mg/kg carboplatin in air-breathing mice.[1] Efaproxiral significantly increases tumor oxygenation by 8.4 to 43.4 mmHg within 5 days in C3H mice with RIF-1 tumors, with maximum increases at 22-31 min after treatment. Efaproxiral plus oxygen plus Radiation produces tumor growth inhibition throughout the treatment duration in C3H mice with RIF-1 tumors, and inhibition is significantly different from radiation plus oxygen from day 3 to day 5. [2] |
| Synonyms | RSR13 sodium |
| Molecular Weight | 363.38 |
| Formula | C20H23NO4·Na |
| CAS No. | 170787-99-2 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 68 mg/mL (187.1 mM)
H2O: 67 mg/mL (184.4 mM)
Ethanol: 68 mg/mL (187.1 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Efaproxiral Sodium 170787-99-2 Immunology/Inflammation Metabolism NF-Κb Reactive Oxygen Species RSR-13 RSR13 RSR 13 RSR13 sodium Inhibitor inhibit Efaproxiral inhibitor
