 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Dihydrorotenone is a potent mitochondrial inhibitor and probably induces Parkinsonian syndrome.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $98 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $277 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $443 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $733 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $987 | - | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $1,330 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $285 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Dihydrorotenone is a potent mitochondrial inhibitor and probably induces Parkinsonian syndrome. |
| In vitro | Dihydrorotenone arrested human plasma cancer cells at the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle. Dihydrorotenone inhibited cyclin D2 transactivation, thus inhibiting its mRNA expression. In addition, Dihydrorotenone upregulated the cell cycle repressors p21 and p53. Dihydrorotenone also increased the phosphorylation level of p53, suggesting the upregulated transactivation function of p53, which was confirmed by the induction of p21, a substrate of activated p53. Moreover, Dihydrorotenone downregulated AKT and ERK phosphorylation, an incentive of cell cycle progression. |
| Molecular Weight | 396.43 |
| Formula | C23H24O6 |
| Cas No. | 6659-45-6 |
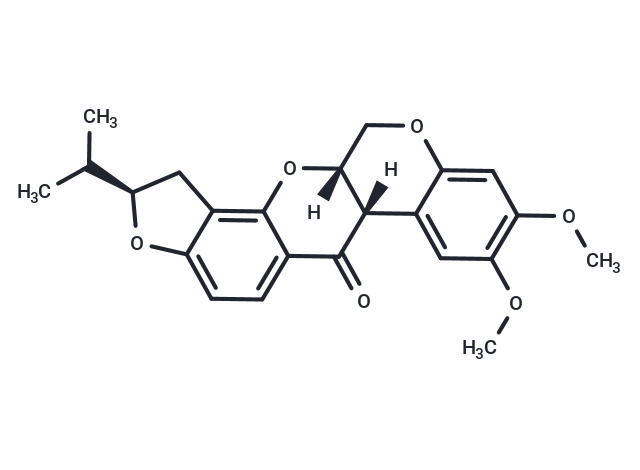
| Smiles | [H][C@@]12COc3cc(OC)c(OC)cc3[C@]1([H])C(=O)c1ccc3O[C@H](Cc3c1O2)C(C)C |
| Relative Density. | 1.251g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,keep away from moisture,store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 27.5 mg/mL (69.37 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+90% Corn Oil: 2 mg/mL (5.05 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.