 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

CC-401 Hydrochloride (CC401 HCl) is a second generation ATP-competitive anthrapyrazolone c-Jun N terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor (Ki of 25 to 50 nM.)with potential antineoplastic activity.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $32 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $73 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $113 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $228 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $355 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $513 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $80 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | CC-401 Hydrochloride (CC401 HCl) is a second generation ATP-competitive anthrapyrazolone c-Jun N terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor (Ki of 25 to 50 nM.)with potential antineoplastic activity. |
| Targets&IC50 | JNK:25-50 nM (Ki) |
| In vitro | CC-401 in combination with chemotherapy demonstrates synergism in colon cancer cell lines, although synergy is not always hypoxia specific.?A more detailed analysis focused on HT29 and SW620 (responsive), and HCT116 (nonresponsive) lines.?In HT29 and SW620 cells, CC-401 treatment results in greater DNA damage in the sensitive cells. |
| In vivo | In vivo, potentiation of bevacizumab, oxaliplatin, and the combination by JNK inhibition was confirmed in HT29-derived mouse xenografts, in which tumor growth delay was greater in the presence of CC-401.?Finally, stable introduction of a dominant negative JNK1, but not JNK2, construct into HT29 cells rendered them more sensitive to oxaliplatin under hypoxia, suggesting differing input of JNK isoforms in cellular responses to chemotherapy. |
| Animal Research | To assess the efficacy of JNK signaling inhibition by CC-401 in anti-angiogenic and oxaliplatin combination therapy in a mouse xenograft model, adult (8-10 weeks of age) female severe combined immunodeficient mice (C.B.17 SCID) were used.?To generate tumors, HT29 cells (1 × 10^6 cells) were injected subcutaneously into the left flank of the mice.?When the tumors reached approximately 200 mm^3, mice were divided into eight groups (eight mice per group) for treatment with bevacizumab , oxaliplatin, CC401, and the appropriate combinations of bevacizumab, oxaliplatin and CC-401.?Mice in the bevacizumab treatment group received 5 mg/kg of bevacizumab by intraperitoneal injection every 3 days for 21 days.?The oxaliplatin treatment group was injected intraperitoneally with 5 mg/kg oxaliplatin per week for 2 weeks.?The CC-401 treatment group was injected intraperitoneally 25 mg/kg for every 3 days.?The combination treatment groups received bevacizumab (every 3 days, 5 mg/kg), oxaliplatin (weekly for 2 weeks, 5 mg/kg), and CC-401 (every 3 days, 25 mg/kg).?The control group received saline intraperitoneally.?Tumor volume and body weight were measured every 3 days.?Tumor volume was calculated using the formula V = AB^2/2, where A is the largest diameter and B is the smallest diameter.?Tumor growth delay was calculated as the difference in the time for control and treated tumors to grow from 200 to 800 mm^3.?For tumor growth delay calculations, mice were continued to receive treatments till the tumor volume reached 800 mm^3.?For immunohistochemistry mice were sacrificed after treatments on day 9 for tumor processing and staining. |
| Synonyms | CC401 HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 424.93 |
| Formula | C22H25ClN6O |
| Cas No. | 1438391-30-0 |
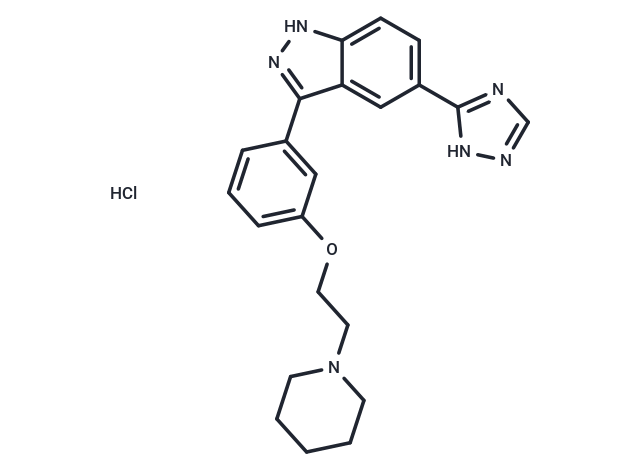
| Smiles | Cl.C(CN1CCCCC1)Oc1cccc(c1)-c1n[nH]c2ccc(cc12)-c1ncn[nH]1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 250 mg/mL (588.33 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 4 mg/mL (9.41 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.