Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Aripiprazole (OPC-14597) is an antipsychotic agent that is structurally related to piperazines and quinolones. It is a partial agonist of SEROTONIN RECEPTOR, 5-HT1A and DOPAMINE D2 RECEPTORS, where it also functions as a post-synaptic antagonist, and an antagonist of SEROTONIN RECEPTOR, 5-HT2A.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $31 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $42 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $58 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $103 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $135 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Aripiprazole (OPC-14597) is an antipsychotic agent that is structurally related to piperazines and quinolones. It is a partial agonist of SEROTONIN RECEPTOR, 5-HT1A and DOPAMINE D2 RECEPTORS, where it also functions as a post-synaptic antagonist, and an antagonist of SEROTONIN RECEPTOR, 5-HT2A. |
| Targets&IC50 | 5-HT1A:4.2 nM(Ki) |
| In vitro | Aripiprazole exhibits the highest affinity for h5-HT(2B), hD(2L), and hD(3) dopamine receptors but also demonstrates significant affinity (5-30 nM) for various other 5-HT receptors (5-HT(1A), 5-HT(2A), 5-HT(7)), as well as α(1A)-adrenergic and hH(1)-histamine receptors. Aripiprazole acts as an inverse agonist at the 5-HT(2B) receptor and displays partial agonist activity at 5-HT(2A), 5-HT(2C), D(3), and D(4) receptors. It binds with high affinity to both G protein-coupled and uncoupled states of these receptors. Additionally, Aripiprazole effectively activates D2 receptor-mediated inhibition of cAMP accumulation. |
| In vivo | Aripiprazole administration at doses of 0.1 mg/kg and 0.3 mg/kg significantly increased dopamine release in the hippocampus of rats. A dose of 0.3 mg/kg slightly, yet significantly, enhanced dopamine release in the medial prefrontal cortex, without affecting dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens. Additionally, 0.3 mg/kg of Aripiprazole transiently amplified dopamine release in the medial prefrontal cortex induced by 0.1 mg/kg of Haloperidol, but it inhibited dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. Higher doses of 3.0 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg distinctly decreased dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens, without impacting the medial prefrontal cortex. Aripiprazole reduced the extracellular concentration of 5-HIAA in the medial prefrontal cortex and striatum of drug-naïve rats, but this effect was not observed in rats with chronic Aripiprazole pretreatment. |
| Synonyms | OPC-14597 |
| Molecular Weight | 448.39 |
| Formula | C23H27Cl2N3O2 |
| Cas No. | 129722-12-9 |
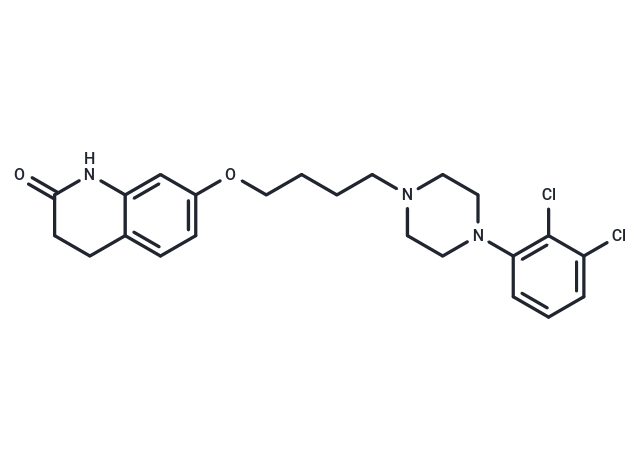
| Smiles | O(CCCCN1CCN(CC1)C2=C(Cl)C(Cl)=CC=C2)C=3C=C4C(=CC3)CCC(=O)N4 |
| Relative Density. | 1.263 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 51 mg/mL (113.74 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (4.46 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.